Fig. 2.
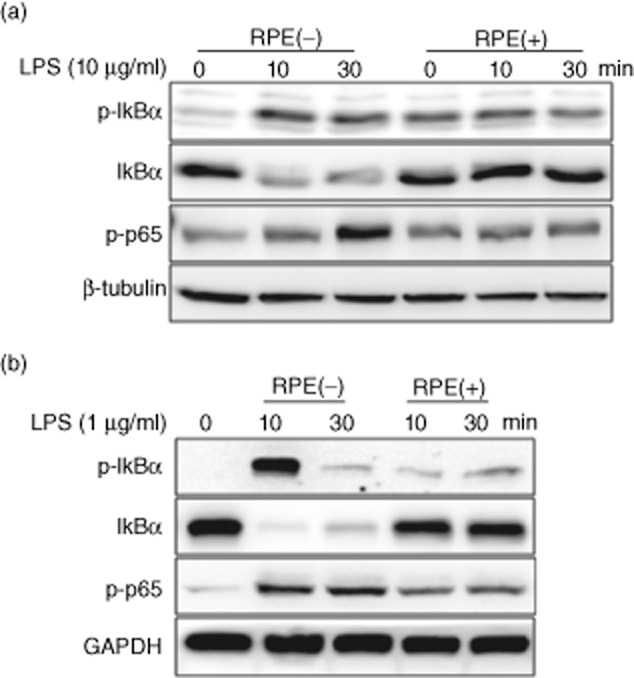
Rice prolamin extract (RPE) inhibits lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced IκBα phosphorylation/degradation and phosphorylation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB/p65 in rat intestinal epithelial cells (RIE) and bone marrow-derived macrophage (BMM). RIE (a) and BMM (b) were pretreated for 1 h with RPE (1000 μg/ml) and then stimulated with LPS (10 μg/ml for RIE and 1 μg/ml for BMM) for 10 and 30 min. IκBα phosphorylation/degradation and phosphorylation of NF-κB/p65 were evaluated by Western blotting. The LPS-induced IκBα phosphorylation/degradation and phosphorylation of NF-κB/p65 were inhibited by co-incubation of LPS with RPE.
