Fig. 4.
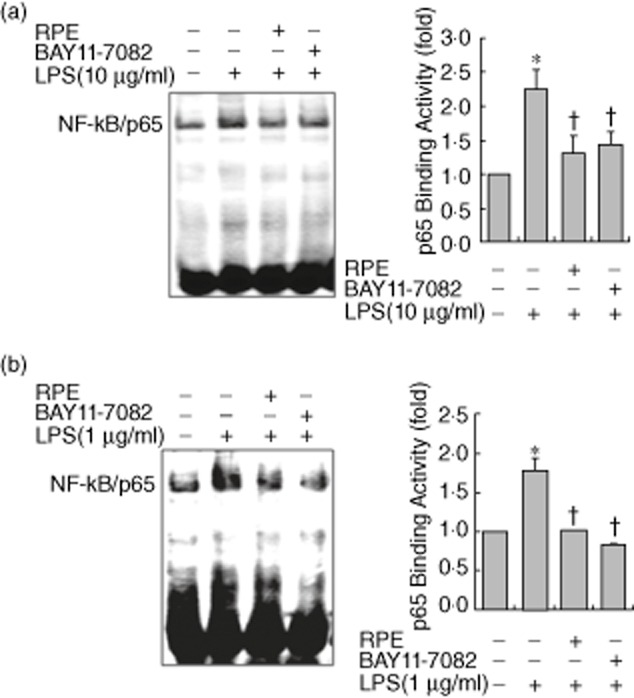
Rice prolamin extract (RPE) inhibits LPS-induced DNA-binding activity of nuclear factor (NF)-κB/p65 in RIE and BMM. RIE (a) and BMM (b) were pretreated for 1 h with RPE (1000 μg/ml) or Bay11-7082 (5 μM) and then stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (10 μg/ml for RIE and 1 μg/ml for BMM) for 30 min. The DNA binding activity of NF-κB was evaluated by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). RPE and Bay11-7082 inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB DNA-binding activity in RIE and BMM. Bars represent the mean ± standard error of the mean from three different experiments (*P < 0·05, compared to unstimulated cells; †P < 0·05, compared to LPS stimulation). RPE, rice prolamin extract; RIE, rat intestinal epithelial cell; BMM, bone marrow-derived macrophage.
