Fig. 10.
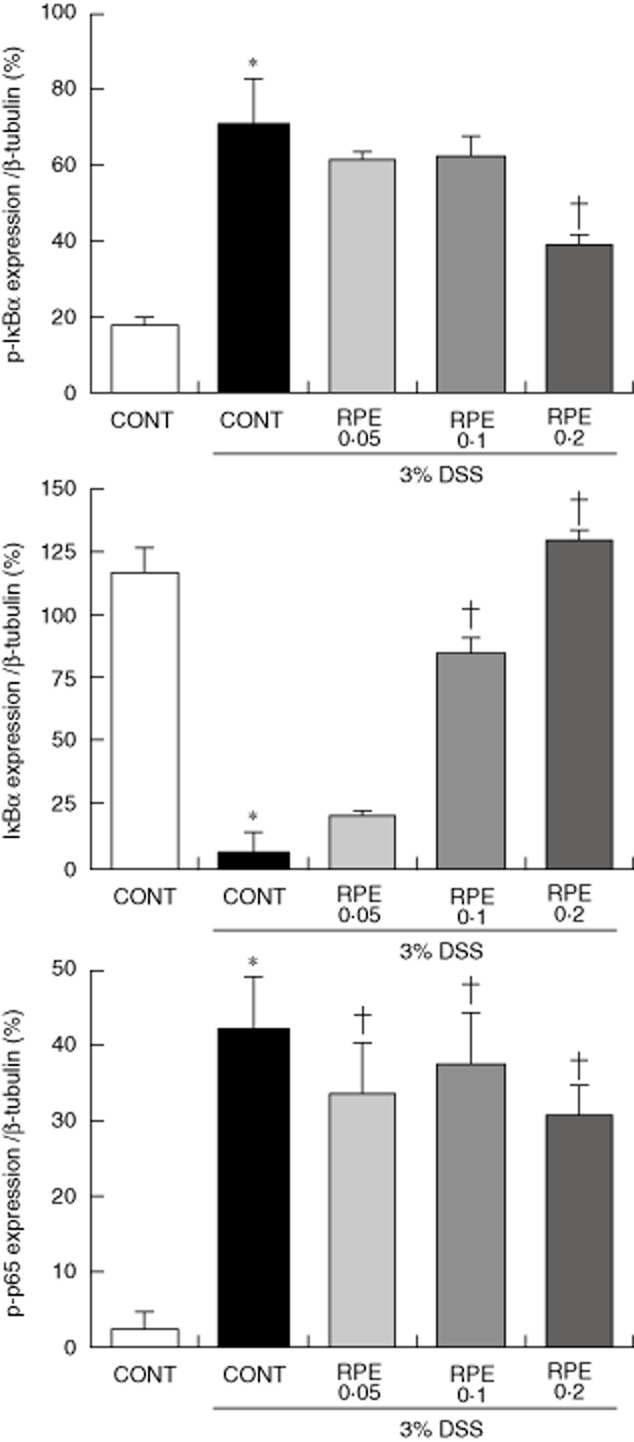
Rice prolamin extract (RPE) inhibits nuclear factor (NF)-κB/p65 activation in dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced experimental colitis. Mice (n = 6 per group) were killed after 6 (for total colon protein) days of 3% DSS exposure, respectively, and protein (20 μg) was subjected to sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Western blotting for IκBα, phospho-IκBα, phospho-p65 and β-tubulin was performed. Band intensities were quantified by densitometry. Results are representative of three independent experiments. DSS-induced IκBα phosphorylation/degradation and phosphorylation of NF-κB/p65 were blocked by RPE (*P < 0·05 versus control; †P < 0·05 versus DSS alone). CONT, control chow.
