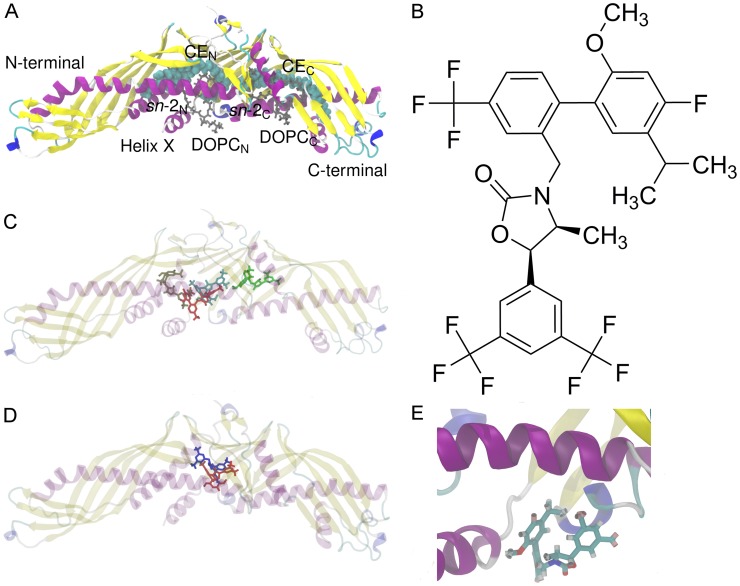
Figure 1. Structures of CETP and anacetrapib and results from molecular docking.
A) X-ray structure of human CETP. The two DOPCs (gray) plug the tunnel openings that lead to the hydrophobic tunnel where two CEs (cyan spheres) are located. The sn-chains of DOPCs, the N- and C-terminals, as well as helix X are labeled. B) The atomic formula of anacetrapib. Anacetrapib is a 1–3-oxazolidin-2-one based CETP inhibitor. C) The most probable binding sites and conformations of anacetrapib within the structure of CETP obtained from molecular docking calculations. The binding energies for the binding sites of red, brown, cyan, and green ligands are −47.7 kJ mol−1, −46.4 kJ mol−1, −48.5 kJ mol−1, and −46.9 kJ mol−1, respectively. D) The most probable binding site of anacetrapib gained from docking calculations matched with the recently published X-ray structure of CETP with bound torcetrapib. Anacetrapib is presented with red and torcetrapib with blue color. E) Simulation snapshot from simulation S2-1nm. While moving at the N-terminal tunnel opening, anacetrapib aligns itself to a tighter conformation through the orientation of trifluoromethyl- and methyl groups close to each other.