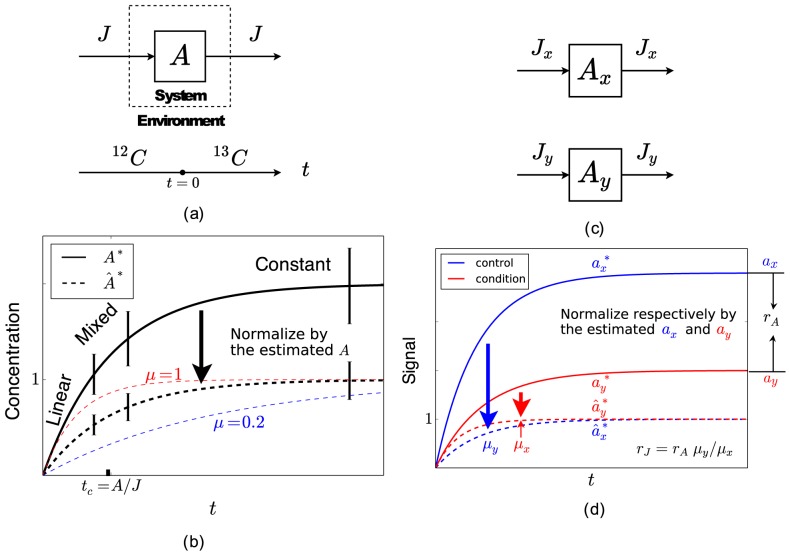
Figure 1. Understanding KFP and rKFP.
(a) A schematic diagram of KFP applied to a toy metabolic network. At 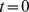 , the system is switched from a
, the system is switched from a 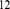 C-labeled environment to
C-labeled environment to 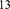 C-labeled one, and
C-labeled one, and 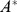 is measured at a few time points thereafter. (b) For a given trajectory of
is measured at a few time points thereafter. (b) For a given trajectory of 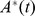 (the black solid curve), the three time regimes (linear, mixed and constant) are marked and three measurements are made (two in the mixed regime and one in the constant). Normalizing it gives
(the black solid curve), the three time regimes (linear, mixed and constant) are marked and three measurements are made (two in the mixed regime and one in the constant). Normalizing it gives 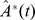 between 0 and 1 (the black dashed curve), parameterized by a single parameter
between 0 and 1 (the black dashed curve), parameterized by a single parameter 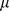 , which can be estimated by comparing the normalized measurements to
, which can be estimated by comparing the normalized measurements to 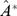 's of different
's of different 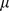 's (the red and blue dashed curves). (c) A schematic diagram of rKFP applied to the same network in (a). Relative quantitation is performed on
's (the red and blue dashed curves). (c) A schematic diagram of rKFP applied to the same network in (a). Relative quantitation is performed on 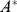 in two conditions (with subscripts
in two conditions (with subscripts  and
and  respectively) with the goal of estimating
respectively) with the goal of estimating 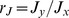 . (d) The ratio in
. (d) The ratio in 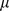 between
between 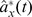 and
and 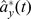 is
is 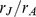 (Eq. 6), and since
(Eq. 6), and since 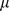 's and
's and 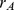 are identifiable from relative quantitation, so is
are identifiable from relative quantitation, so is 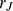 .
.