Fig. 4. Two-dimensional DNA-forest XY-crystals.
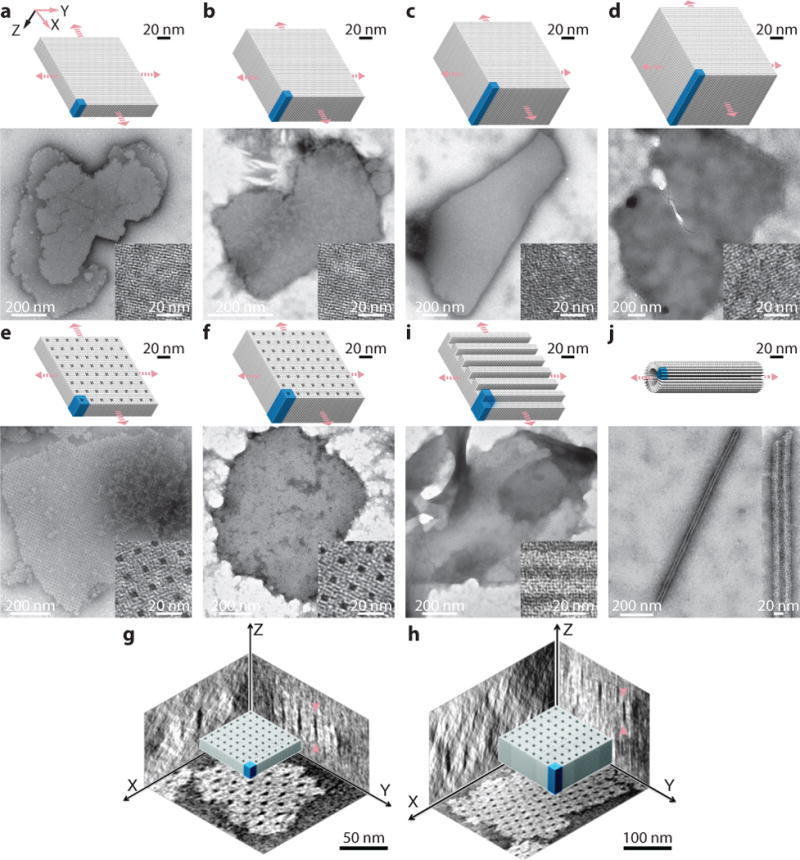
Cylinder models (top) and TEM images (bottom) are shown for each crystal. a to d, Solid XY-crystals: 64B (a), 128B (b), 192B (c), and 256B (d) solid XY-crystals designed from a 4H×4H cuboid. e and f, XY-crystals with pores: a 32×64B-pore XY-crystal with 2H×2H×64B parallel pores (e) and a 32H×128B-pore XY-crystal with 2H×2H×128B parallel pores (f). g and h, Cryo-EM 3D reconstruction images showing the three projections of the XY-32H×64B-pore crystal (g) and the XY-32H×128B-pore crystal (h). Arrows indicate the positions for thickness measurements. i, A 96B XY-crystal with 4H×32B parallel channels. j, A tube crystal formed by 32B helices with helical axis perpendicular to the tube axis. Unit cells of crystals are denoted using blue-colored boxes. See Supplementary Figs. S25 to S34 for more TEM images.
