FIGURE 1.
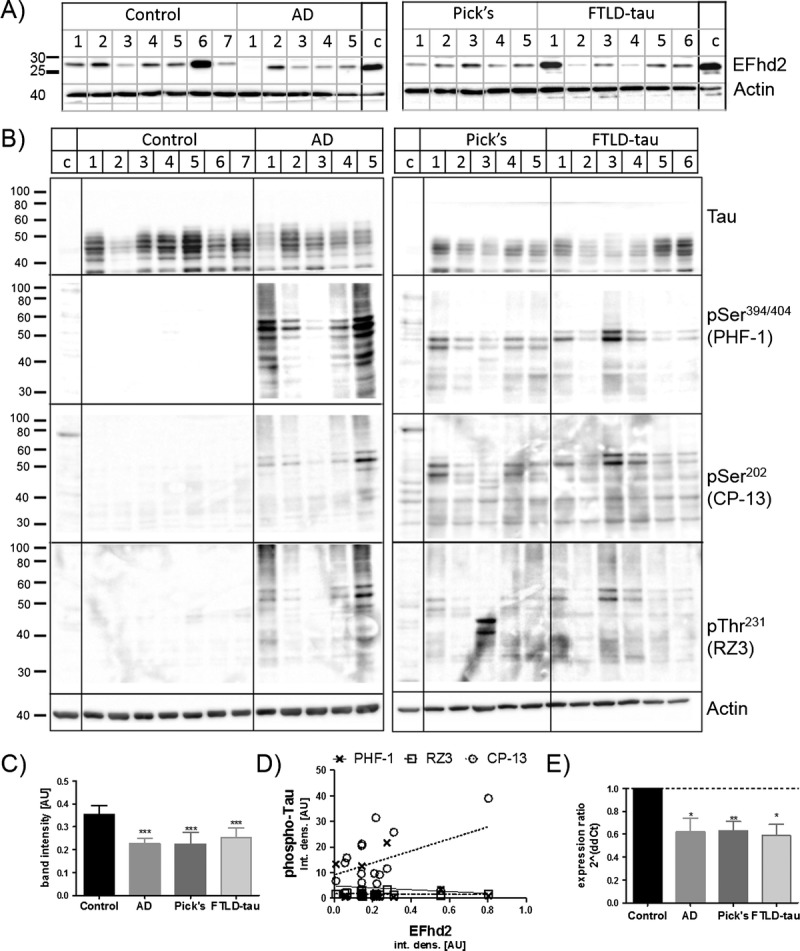
EFhd2 protein levels in the frontal cortex are reduced in tauopathies. (A) Western blot images of EFhD2 in human frontal cortex tissue RIPA buffer extracts from nondemented controls, individuals with Alzheimer disease (AD), Pick disease (Pick’s), and frontotemporal dementia with tau mutations (FTLD-tau). Western blots run with a 293T-cell line lysate loaded as a calibrator on each gel. Beta-actin was used as a loading control. (B) Western blot analysis of total and phosphorylated Tau protein in human frontal cortex samples. (C) Quantification of EFhd2 protein bands by densitometry, n = 3 for each sample. Error bars = SEM. *** p < 0.001 compared with control with 1-way ANOVA and Dunnett post hoc test. (D) Scatter plots of densitometry values for EFhd2 against values for each of the phosphorylated Tau antigens (PHF-1, CP-13, RZ3). Linear regression was done in GraphPad prism and showed no correlation between EFhd2 and any of the phospho-tau antigens. (E) Quantitative real-time PCR for EFhd2, quantified by the ΔΔ-Ct method. Actin and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase were used as housekeeping genes. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 compared with control with 1-way ANOVA and Dunnett post hoc test.
