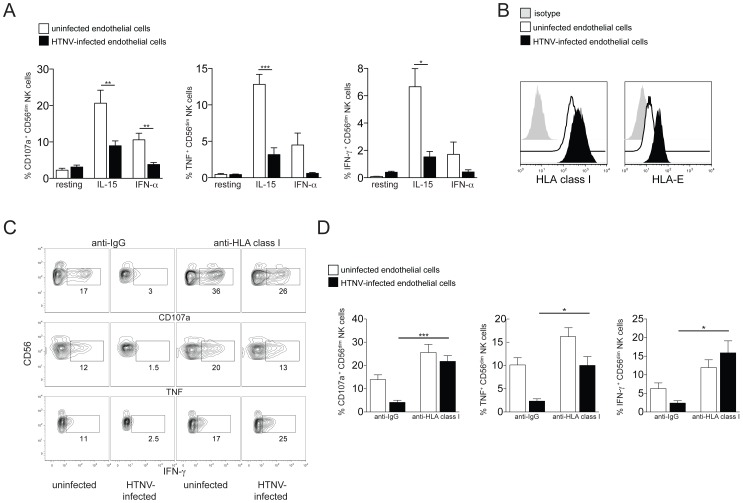
Figure 5. Increased HLA class I expression on hantavirus-infected cells inhibits NK cell effector functions.
(A) Degranulation (CD107a) and cytokine production (TNF and IFN-γ) of resting, IL-15 and IFN-α pre-activated CD56dim NK cells reactive against uninfected (white) or HTNV-infected (black) endothelial cells. Results from 2 independent experiments (n = 6) (*** p≤0.001, ** p≤0.01, * p≤0.05; paired t-test). (B) Representative staining of HLA class I and HLA-E expression on uninfected (white) or HTNV-infected (black) endothelial cells. Isotype control (grey). (C and D) CD56dim NK cell responses against uninfected and HTNV-infected endothelial cells in the presence of anti-HLA class I or isotype control antibody. (C) Representative FACS analysis of the NK cell responses against uninfected and HTNV-infected endothelial cells in the presence of anti-HLA class I or isotype control antibody is depicted. (D) Frequency of CD56dim NK cells expressing CD107a (n = 6), TNF (n = 3) and IFN-γ (n = 3) in response to uninfected (white) and HTNV-infected (black) endothelial cells in the presence of anti-HLA class I or isotype control antibody (*** p≤0.001, * p≤0.05; paired t-test).