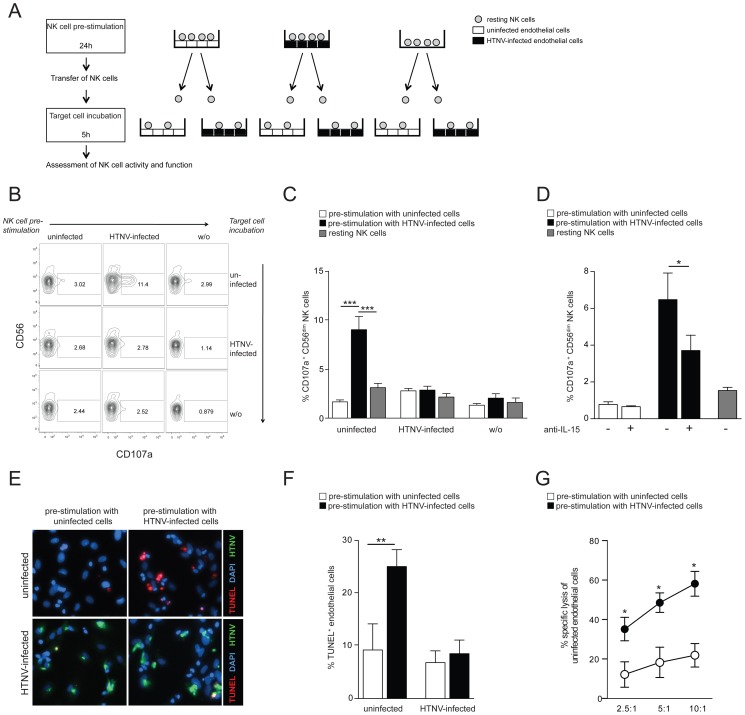
Figure 6. Hantavirus-activated CD56dim NK cells kill uninfected but not hantavirus-infected endothelial cells.
(A) Experimental set-up: NK cells were incubated with uninfected or HTNV-infected cells for 24 h then transferred and incubated for another 5 h with uninfected or HTNV-infected cells, followed by assessment of NK cell degranulation and cytotoxicity. (B and C) Degranulation (CD107a) of CD56dim NK cells pre-stimulated with uninfected or HTNV-infected endothelial cells against uninfected and HTNV-infected endothelial cells. (B) FACS analysis of one NK cell donor is shown. (C) CD107a expression on CD56dim NK cells (n = 9) in response to uninfected and HTNV-infected endothelial cells after pre-stimulation with uninfected (white) or HTNV-infected (black) endothelial cells or medium alone (grey). Results from 3 independent experiments (*** p≤0.001; paired t-test). (D) Degranulation of CD56dim NK cells (n = 4) against uninfected endothelial cells after pre-stimulation with uninfected (white) and HTNV-infected (black) endothelial cells. When indicated, IL-15 was blocked on endothelial cells during pre-stimulation. Results from 2 independent experiments (* p≤0.05; paired t-test). (E and F) Induction of apoptosis in endothelial cells exposed to NK cells pre-stimulated with uninfected or HTNV-infected endothelial cells. (E) One representative immunofluorescent staining is depicted: DAPI (blue), HTNV-nucleocapsid protein (green), TUNEL-positive cells (red). (F) Percentage of TUNEL-positive uninfected and HTNV-infected endothelial cells after exposure to NK cells (n = 6) pre-stimulated with uninfected (white) and HTNV-infected (black) endothelial cells. Results from 3 independent experiments (** p≤0.01; paired t-test). (G) NK cell-mediated specific lysis of uninfected endothelial cells after pre-stimulation with uninfected (white) or HTNV-infected (black) endothelial cells. Depicted are mean values (+/− SD) from 5 donors and 2 independent experiments (* p≤0.05).