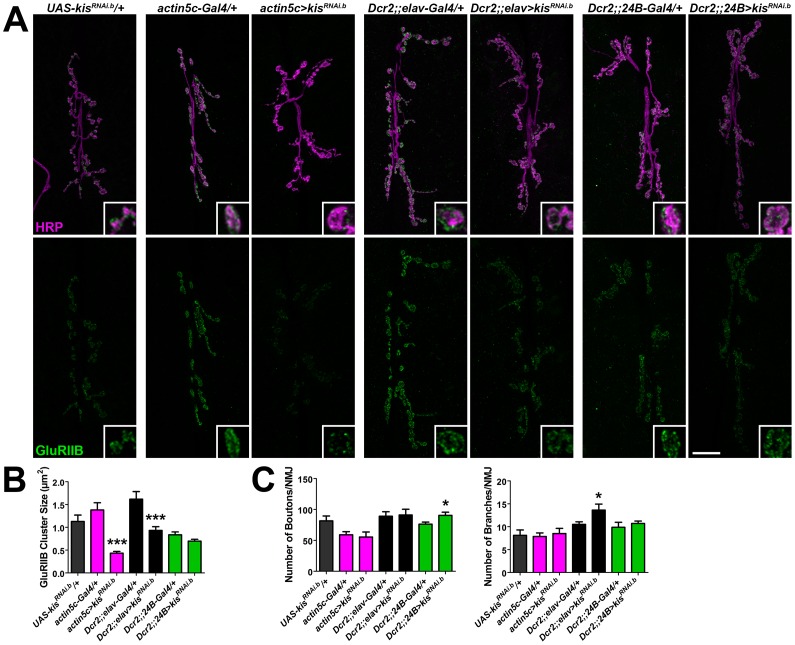
Figure 6. Kis is important pre- and postsynaptically for NMJ development.
(A) Confocal micrographs of third instar larval 6/7 NMJs immunolabled with α-HRP (magenta) and α-GluRIIB (green). Insets show high magnification image of a single terminal bouton. Scale bar = 20 µm. (B) Quantification of GluRIIB cluster size in µm2 in genotypes listed indicates that knockdown of kis in all cells or presynaptic neurons but not postsynaptic muscles results in a significant reduction in GluRIIB cluster size. (C) Quantification of the number of 6/7 NMJ boutons (left) and branches (right) in the genotypes listed.