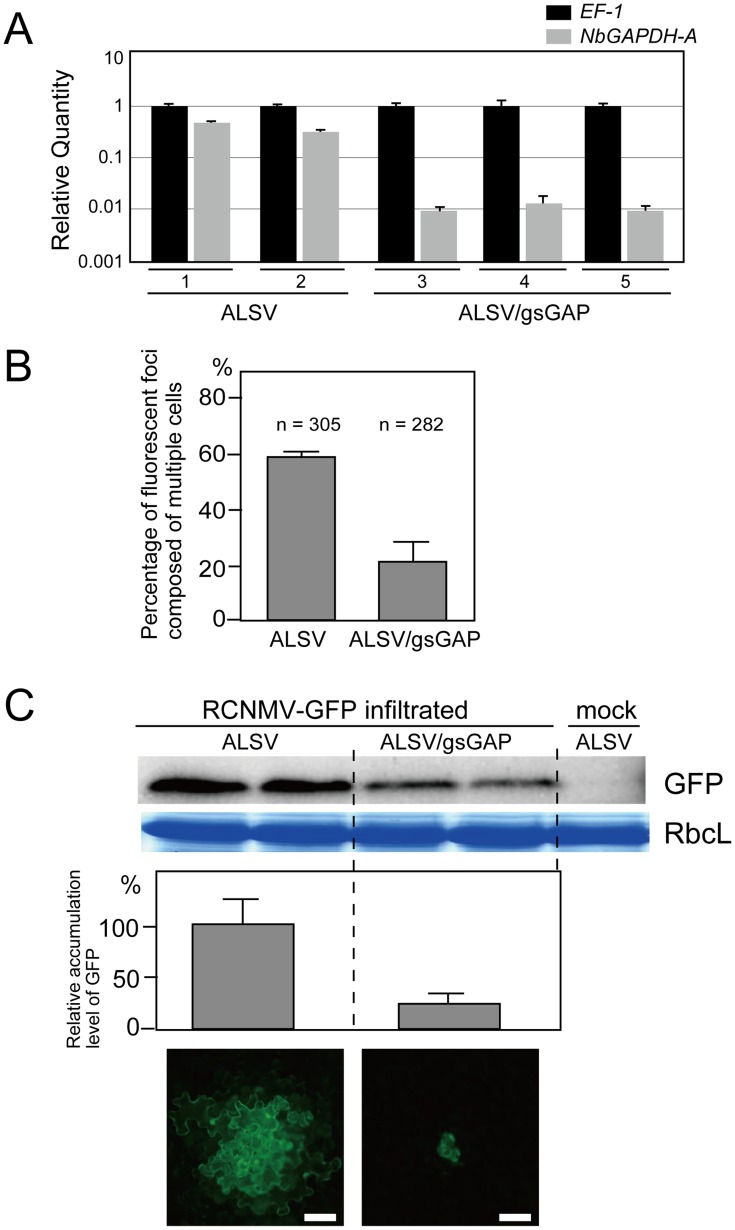
Figure 3. Multiplication of RCNMV is inhibited in NbGAPDH-A-silenced N. benthamiana leaves.
(A) Gene silencing of NbGAPDH-A was induced in N. benthamiana plants inoculated with the ALSV vector, which harbored a 294 bp partial fragment (nucleotides 352–645 from start codon) of NbGAPDH-A (ALSV/gsGAP), via Agrobacterium. The empty ALSV vector (ALSV) was used as a control. Total RNA was prepared from two ALSV-infected and three ALSV/gsGAP-infected plants. NbGAPDH-A mRNA levels were determined by real time PCR using primers specific to NbGAPDH-A (nucleotides 755–954 from start codon). The real time PCR results for the EF-1 mRNA (closed column) were used to adjust the relative accumulation levels of NbGAPDH-A mRNA (gray column). (B) In vitro transcripts of a recombinant RCNMV that expressed GFP from its subgenomic RNA (RCNMV-GFP, Figure S1E) were inoculated mechanically onto ALSV- or ALSV/gsGAP-infected N. benthamiana plants. At 20 hpi, the percentages of fluorescent foci that comprised multiple cells were measured using epifluorescence microscopy. ‘n’ represents the total number of fluorescent foci in 4 inoculated leaves (about 25 square centimeters). (C) An Agrobacterium culture that contained the pBICR1sG2 plasmid, which expressed RCNMV-GFP (Figure S1F), was diluted to OD600 = 0.03 and infiltrated into ALSV- or ALSV/gsGAP-infected N. benthamiana plants. At 35 hpi, protein was extracted from the infiltrated leaves and subjected to Western blotting using anti-GFP antibody. RbcL is a Coomassie brilliant blue-stained gel image, which shows the large subunit of Rubisco proteins. The accumulated levels of GFP from three separate experiments were quantified using the Image Gauge program and plotted in the graph. The lowest two panels show representative epifluorescence microscopy images of the infiltrated leaves at 35 hpi. Scale bar = 50 µm.