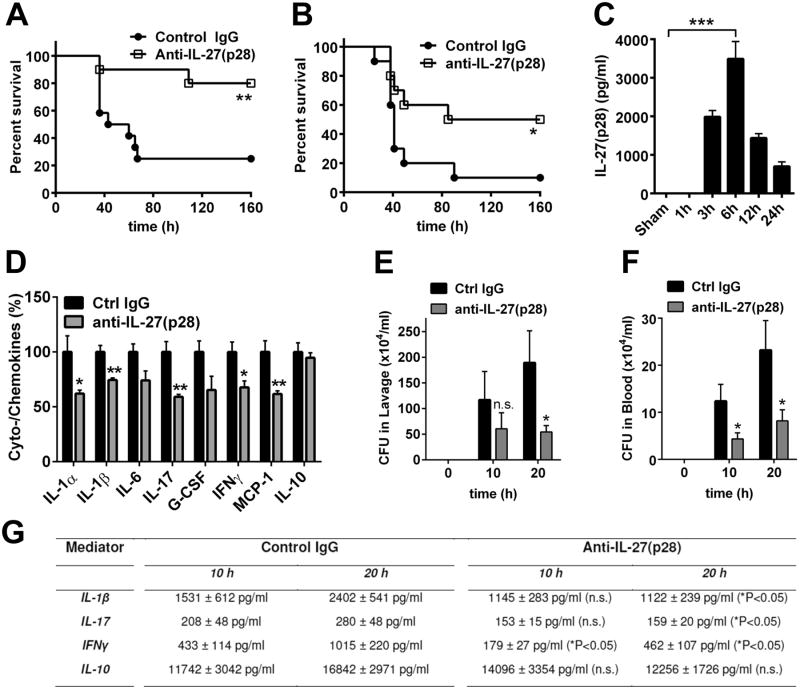
Figure 1. Neutralization of IL-27(p28) is protective during polymicrobial sepsis and endotoxic shock.
A. Survival of Wt mice during endotoxic shock (LPS 10 mg/kg body weight i.p.) following treatment with neutralizing anti-IL-27(p28) antibody (40 μg/mouse i.p., n=10) or control IgG (40 μg/mouse i.p., n=12). B. Survival of Wt mice after CLP (‘high-grade’) with treatment of either control IgG or neutralizing anti-IL-27(p28) antibody (40 μg/mouse i.p., n=10 for both groups). C. Time course for appearance of IL-27(p28) in plasma of Wt mice during endotoxic shock, n=4-6 mice for each time point, ELISA. D. Reduction of plasma mediators during endotoxic shock in Wt mice using control IgG or anti-IL-27(p28) antibody (n=5/group), 12 h, bead-based assay. E. Quantification of colony forming units (CFU) in peritoneal lavage fluids of Wt mice at different time points after CLP with application of control IgG or blocking anti-IL-27(p28) antibody (40 μg/mouse i.p., n=10 for both groups). F. Determination of bacteremia (CFU) in blood from the same experiment described under E. G. Detection of plasma mediators after 10 h and 20 h following CLP in Wt mice treated with neutralizing anti-IL-27(p28) antibody or control IgG (n≥7/group). Antibodies were injected 1 h before CLP or LPS in all experiments. All experiments were performed with the numbers of mice per group as indicated. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, n.s. denotes not significant.