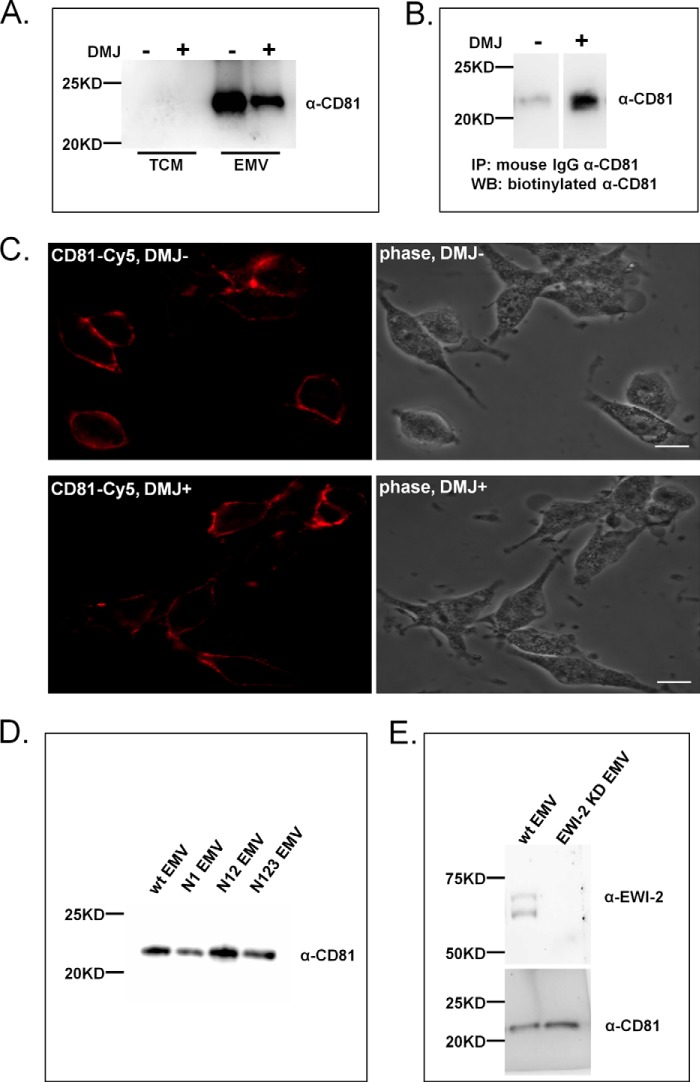
FIGURE 5.
CD81 recruitment to EMV is glycan-dependent but not EWI-2-dependent. A, inhibition of complex N-glycan alters CD81 trafficking to EMV. Sk-Mel-5 cells were treated with DMJ (1 mm) for 48 h before collection of TCM or EMV (+ DMJ). Untreated Sk-Mel-5 cells were used as a control (− DMJ). TCM and EMV samples (+/− DMJ) were probed for CD81. Equal amounts of TCM samples (25 μg of protein) and of EMV (10 μg of protein) were compared by SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. Western blots shown are representative of two biological replicates. B, CD81 was immunoprecipitated from equal amounts (by protein) of DMJ-treated and -untreated TCM samples. Immunoprecipitated samples were run on SDS-PAGE then analyzed for CD81 by Western blot analysis with a different α-CD81 antibody than that used for immunoprecipitation. Western blots shown are representative of two biological replicates. C, cell surface localization of CD81 is not affected by DMJ treatment. Sk-Mel-5 cells were treated with either DMJ (1 mm, DMJ +) or buffer (DMJ −) for 48 h. The cells were fixed and stained with an α-CD81 antibody (α-CD81 biotin, Cy5-α-biotin mAb, red). Cells were imaged with fluorescence microscopy. The scale bar is 20 μm. D, Sk-Mel-5 cells were transfected with WT, N1, N12, and N123 EWI-2-FLAG constructs, and TCM samples were collected. EMV samples were isolated from culture media. Equal amounts of TCM samples (25 μg of protein) and EMV (10 μg of protein) samples were loaded onto SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot analysis for CD81. Western blots shown are representative of three biological replicates. E, a stable EWI-2 knockdown of the Sk-Mel-5 cell line was generated using lentiviral stocks of shRNA. EMV samples were isolated from the EWI-2 knockdown cell line (EWI-2 KD) or from parent Sk-Mel-5 (WT). Equal amounts of EMVs (10 μg) were resolved using SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blot analysis for EWI-2 and CD81. Western blots shown are representative of three independent EMV isolations from this cell line.