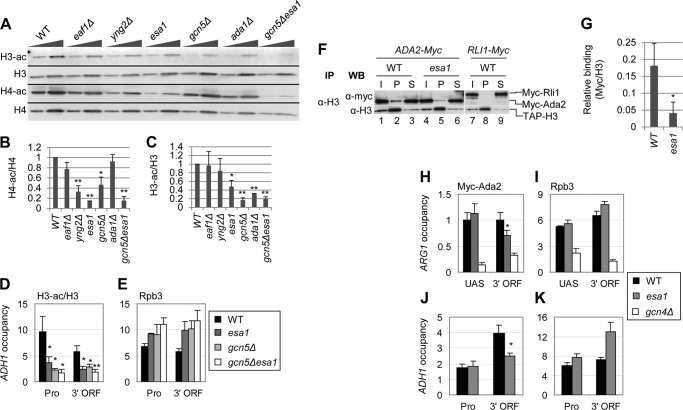
FIGURE 4.
NuA4 stimulates H3 acetylation by SAGA. A–C, effect of NuA4 and SAGA subunit mutations on H3 and H4 acetylation. Strains (BY4741, DGY326, DGY304, DGY150, 7285, 1038, and DGY154) were grown in YPD at 30 °C, transferred to 36 °C for 4 h, and WCEs were subjected to Western analysis with antibodies against diacetylated H3, the H3 C terminus, tetra-acetylated H4 and H4 C terminus. In B and C, acetylation per histone was calculated as the ratio of the acetylated histone signal to the total histone signal for each strain (n = 4). Strains in which H3 or H4 acetylation was determined to be significantly reduced compared with WT as calculated by Student's t test are indicated by asterisks (*, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001). D and E, ChIP analysis of H3-ac (D) and Rpb3 (E) at ADH1. WT and KAT mutant strains (BY4741, DGY150, and DGY154) were grown in YPD at 30 °C, transferred to 36 °C for 1 h, and ChIP was performed using antibodies to diacetylated H3, H3 (D), and Rpb3 (E) and PCR primers to amplify the ADH1 promoter and 3′ ORF, a region of the chromosome VI telomere (Tel VI) (D), and chromosome V (Chr V) (E). H3-ac/H3 occupancy was calculated as the ratio of H3-ac occupancy to H3 occupancy. H3-ac/H3 in the KAT mutants was determined to be significantly less than WT by Student's t test (*, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001). F and G, coimmunoprecipitation of Myc-Ada2 with H3. Myc-ADA2 or Myc-RLI1 strains (HQY392, DGY365, and YDH353) were grown in YPD at 30 °C and transferred to 36 °C for 1 h. WCEs were immunoprecipitated with anti-H3 antibodies and subjected to Western analysis with anti-H3 and anti-Myc antibodies. In G, relative binding was calculated as the ratio of Myc pellet to supernatant signal divided by the H3 pellet signal. Relative binding in esa1 cells was determined to be significantly less than in WT cells by Student's t test (*, p < 0.01). H–K, ChIP analysis of Myc-Ada2 (H and J) and Rpb3 (I and K) at ARG1 (H and I) and ADH1 (J and K). WT, esa1, and gcn4Δ strains (HQY392, DGY365, and HQY503) were grown in SC at 30 °C, transferred to 36 °C for 30 min, treated with 0.6 μm SM for 30 min, and ChIP was performed using anti-Myc (H and J) and anti-Rpb3 (I and K) antibodies and PCR primers to the ARG1 UAS and 3′ ORF (H and I), the ADH1 promoter and 3′ ORF (J and K), and Chr V. Myc-Ada2 3′ ORF occupancy in esa1 was determined to be significantly less than WT by Student's t test (*, p < 0.01).