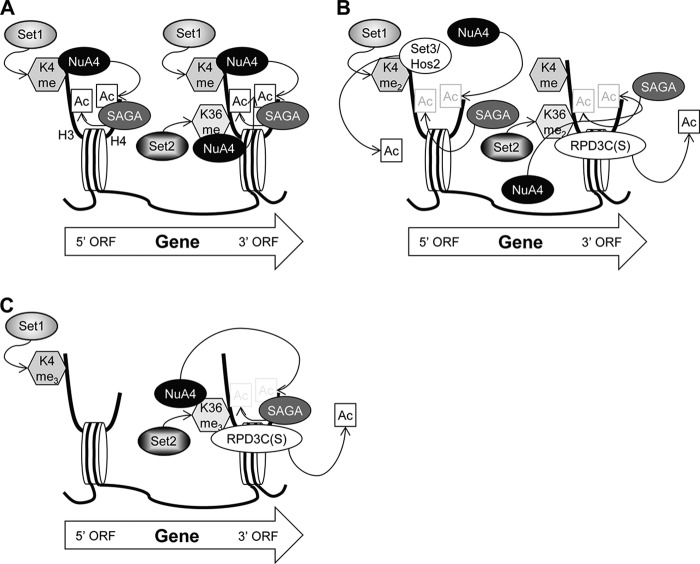
FIGURE 7.
H3K4 and H3K36 methylation regulates H3 and H4 acetylation and deacetylation during transcription elongation. A, nucleosomes monomethylated on H3K4 by Set1 or H3K36 by Set2 (depicted by dotted arrows) are bound by NuA4, which acetylates the H4 tail (H4-ac). Nucleosomes containing H4-ac are bound by SAGA, which acetylates the H3 tail (H3-ac). NuA4 interaction with nucleosomes and attendant H4-ac formation, SAGA recruitment, and H3-ac depends primarily on Set1 and H3K4me in the 5′ end of CDS and Set2/H3K36me further downstream. B, on dimethylated nucleosomes, HDACs Set3/Hos2 and RPD3C(S) compete with NuA4 for binding to H3K4me2 and H3K36me2, respectively. As HDACs can now interact with these nucleosomes, acetylation is reduced. C, neither NuA4 nor Set3/Hos2 interacts with H3K4me3 in the 5′ ORF, whereas NuA4 and RPD3C(S) continue to oppose each other by interacting competitively with H3K36me3 at the 3′ ORF.