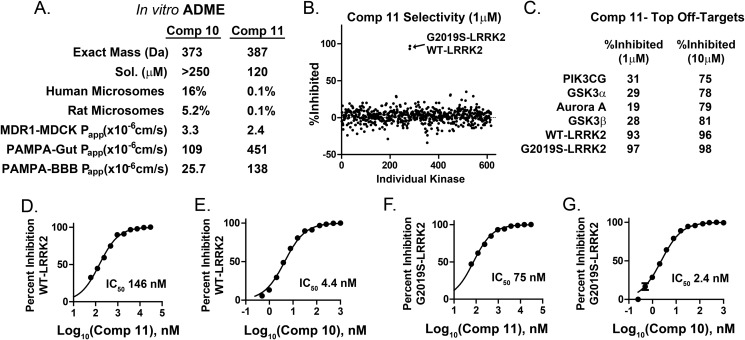
FIGURE 5.
Drug properties, selectivity, and potency of TPZ compounds. A, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) characteristics of two selected TPZ compounds (Comp) that demonstrate superior solubility (Sol) but poor rat and human liver microsome stability, with percent unmodified compound given after 1 h in the presence of NADPH+. In NADPH− reactions, 100% of compound remained after 1 h in all experiments. Corresponding mass spectrometry analyses of NADPH+ metabolites are given in supplemental Fig. 3. Apparent membrane permeability constants (Papp) are given from MDR1-MDCK and Caco-2 permeability assays (gut) and blood-brain barrier (BBB) parallel artificial membrane permeation assays (PAMPA). B, compound 11 was evaluated at 1 μm (shown) and 10 μm in commercial kinase assays involving the entire constituencies of the kinase collections available through EMD Millipore and Invitrogen. All assays were performed at Km(ATP) of the respective kinase. C, three kinases other than WT or G2019S-LRRK2 (glycogen synthase kinase 3, aurora kinase A, and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase γ) were inhibited more than 50% at 10 μm as indicated. D–G, relative potencies of compounds 10 and 11 in LRRK2 cis-autophosphorylation kinase assays. The indicated values were derived from at least three independent assays.