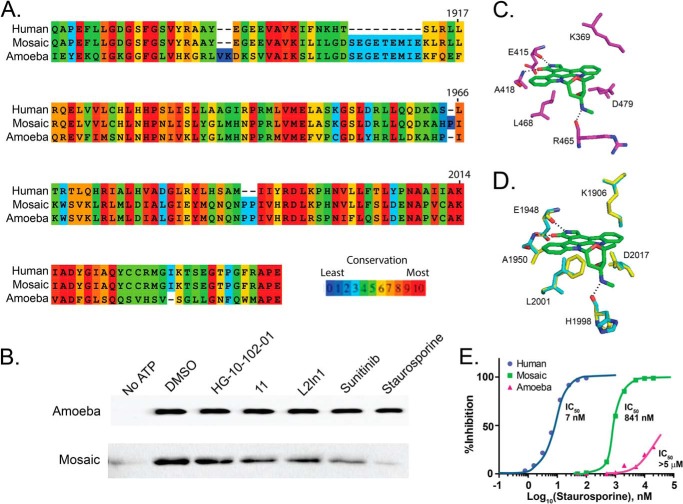
FIGURE 9.
Creation of a humanized LRRK2 ATP-binding pocket from the ameba LRRK2 kinase domain. A, sequence alignment of the human and ameba LRRK2 kinase domains together with the selected artificial mosaic sequence that substitutes human LRRK2 ATP pocket residues into the ameba scaffold. B, kinase assays measuring autophosphorylation as detected by immunoblot analysis with a Thr(P) antibody. Autophosphorylation of the ameba LRRK2 kinase domain is not impaired by 10 μm treatment of the indicated kinase inhibitor. The mosaic protein is also kinase-active and becomes sensitive to LRRK2 kinase inhibitors, with staurosporine inhibiting the largest amount of activity. C, stereotypical binding of a promiscuous ATP-competitive small molecule, staurosporine (green), to the ZAP-70 protein kinase domain (purple). Residues involved in hydrogen bonding are colored by elements (red, oxygen; blue, nitrogen). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. D, best fit model of staurosporine interaction in the ameba LRRK2 homolog. Docking to the ATP pocket demonstrates a critical steric clash of the Phe equivalent to human LRRK2 Leu-2001. The conserved Asp-2017 and Lys-1906 show a steric clash with staurosporine in ameba LRRK2 and, to a lesser extent, mosaic LRRK2. E, inhibition profiles of staurosporine in blocking autophosphorylation activity of human LRRK2, mosaic LRRK2, and ameba LRRK2, with IC50 values given.