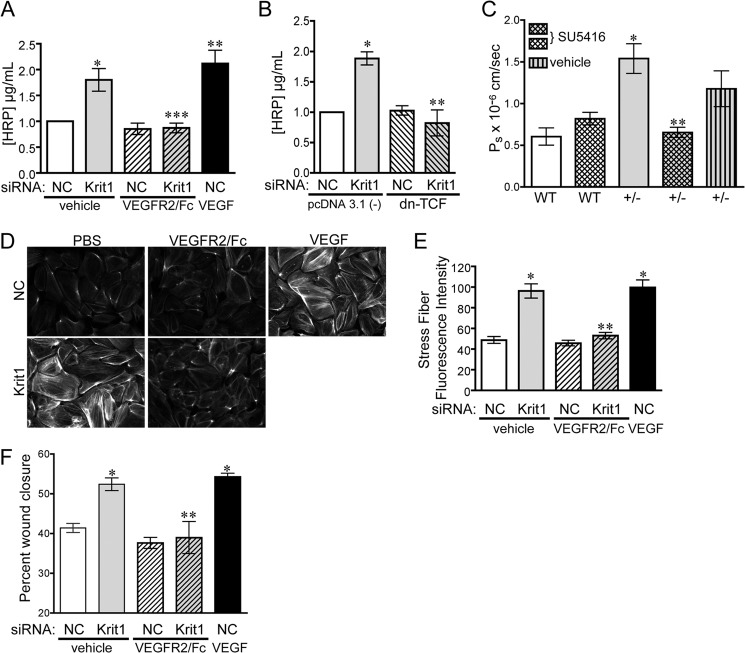
FIGURE 3.
Loss of KRIT1 leads to VEGF-dependent barrier disruption and migration. A, HRP leak through BAEC monolayers transfected with NC- or KRIT1-siRNA ± 25 ng/ml VEGFR2/Fc or recombinant human VEGF (50 ng/ml). Data shown are the mean HRP concentration, ± S.E. n = 3, p = 0.0005 by ANOVA; *, p < 0.05 by post-hoc testing versus NC-transfected cells; **, p < 0.01 versus NC-transfected cells; ***, p < 0.01 versus KRIT1. B, HRP leak through BAEC monolayers transfected with NC- or KRIT1-siRNA, ± co-expression of dn-TCF. Data shown are the mean HRP concentration ± S.E; n = 3; p = 0.001 by ANOVA; *, p < 0.01 by post-hoc test versus NC; **, p < 0.01 versus KRIT1 siRNA-transfected cells. C, cremaster microvessel permeability in WT or Krit1+/− (+/-) mice treated ± 3 mg/kg SU5416 or with vehicle alone. Data shown are the mean Ps ± S.E. n ≥ 17 vessel sites; p < 0.0001 by non-parametric ANOVA; *, p < 0.001 by post-hoc testing versus WT; **, p < 0.001 versus +/−. D, epifluorescence images of rhodamine-phalloidin-stained NC and KRIT1-siRNA-transfected HPAE-treated ± 25 ng/ml VEGFR2/Fc or 50 ng/ml rhVEGF. Images are representative of three separate experiments; scale bar = 50 μm. E, fluorescent intensity quantification of D. n ≥ 40 cells from 10 fields of view ±S.E. p < 0.0001 by ANOVA; *, p < 0.001 by post-hoc test versus NC-transfected cells; **, p < 0.001 versus KRIT1 siRNA-transfected cells. F, percent wound closure of NC- and KRIT1-siRNA-transfected cells treated ± 25 ng/ml VEGFR2/Fc or 25 ng/ml rhVEGF. Data shown are the mean ± S.E. n = 8; p < 0.0001 by ANOVA; *, p < 0.001 by post-hoc test versus NC-transfected cells; **, p < 0.001 versus KRIT1-siRNA-transfected cells.