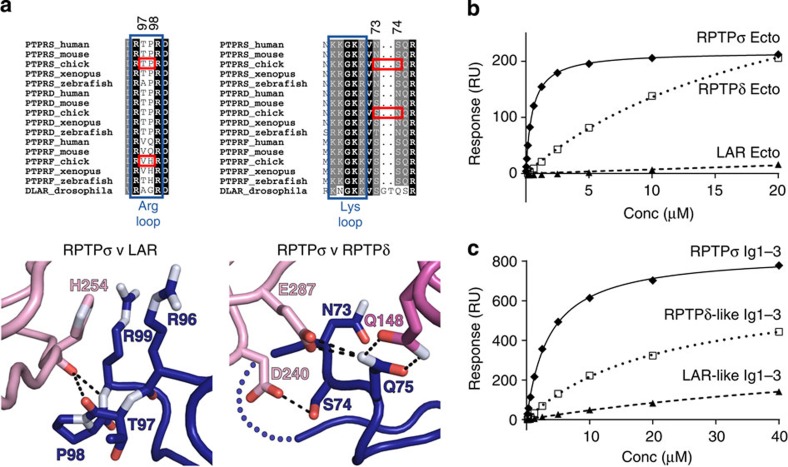
Figure 3. TrkC binding preferences for type IIa RPTP family members.
(a) Type IIa RPTP sequence alignments and detailed views of the RPTPσ:TrkC crystal structure at binding site 1 (left) and binding site 2 (right). Blue boxes indicate RPTPσ residues required for proteoglycan binding, and red boxes highlight key sequence differences conferring TrkC-binding specificity. Colour scheme as in Fig. 2: dark blue, RPTPσ Ig1; pink, TrkC LRR; magenta, TrkC Ig1. (b) SPR analysis of human type IIa RPTP ectodomains binding to immobilized mouse TrkC LRRIg1. Measured binding values: RPTPσ Ecto, Kd=516 nM and Bmax=217 RU; RPTPδ Ecto, Kd>22 μM and Bmax>433 RU; RPTP LAR, Kd and Bmax not determined. (c) SPR analysis of chicken TrkC LRRIg1 binding to immobilized chicken RPTPσ Ig1–3, RPTPσ N73S+S74N (RPTPδ-like) Ig1–3 and RPTPσ P97V+T98H (LAR-like) Ig1–3. Measured binding values: RPTPσ Ig1–3, Kd=3.5 μM and Bmax=837 RU; RPTPδ-like Ig1–3, Kd>21 μM and Bmax>674 RU; RPTP LAR-like Ig1–3, Kd and Bmax not determined. For sensograms see Supplementary Fig. 8a,b.