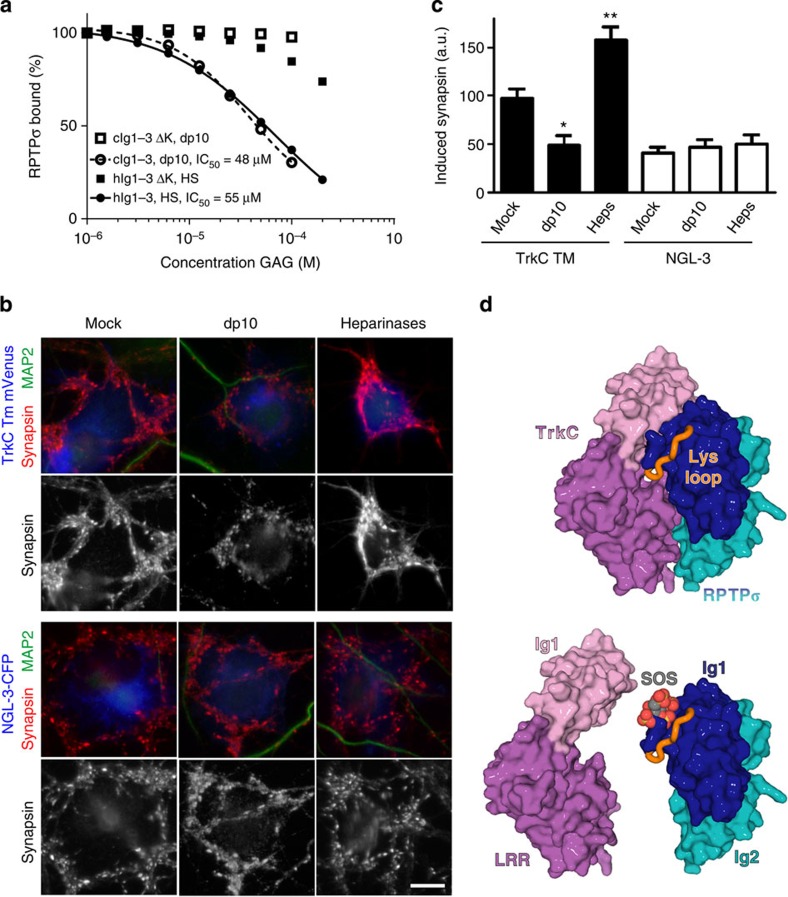
Figure 6. GAG-mediated inhibition of synaptic RPTPσ:TrkC interaction and function.
(a) SPR analysis of human RPTPσ Ig1–3 and RPTPσ Ig1–3 ΔK binding to immobilized mouse TrkC LRRIg1 in the presence of increasing concentrations of HS or heparin-dp10. For sensograms see Supplementary Fig. 10a,b. (b,c) Induced synapsin clustering in rat hippocampal neurons by COS-7 cells expressing TrkC TM or NGL-3 in the presence of heparin-dp10, heparinases (Heps) or mock control. Analysis of variance P<0.0001, *P<0.01 and **P<0.001 compared with TrkC TM mock, whereas NGL-3 heparin-dp10 or heparainase groups were not significantly different from NGL-3 mock by post hoc Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test, n=16–26 cells from two experiments. Scale bar, 10 μM. (d) Illustration of the partial overlap between GAG- and TrkC-binding sites on RPTPσ. Top panel: the RPTPσ:TrkC complex, rotated 180° around the y axis relative to Fig. 2b. Lower panel: sucrose octasulphate (SOS, grey/red) is modelled in the RPTPσ GAG-binding site, an equivalent location to that observed in the LAR:SOS co-crystal structure (which is homologous with RPTPσ, PDB ID: 2YD8). SOS (or GAG) binding can out-compete the TrkC interaction with RPTPσ.