Figure 1. Oxidative Stress and Mitochondrial Dysfunction [48].
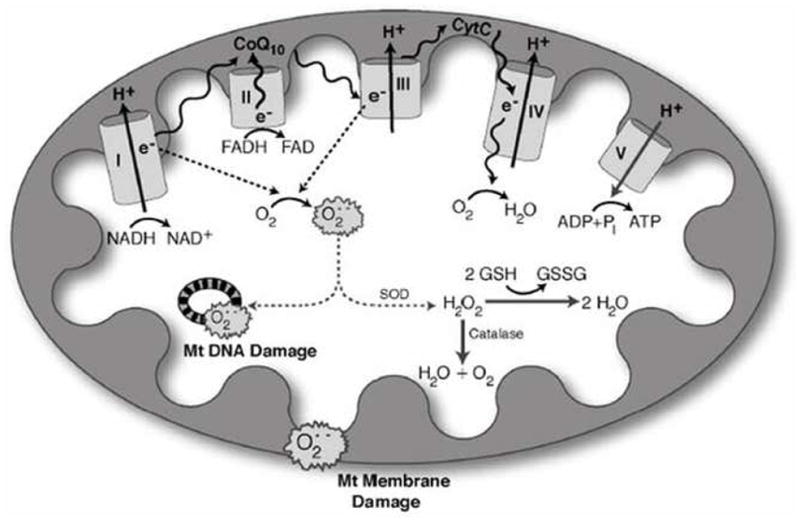
Hyperglycemia increases production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in mitochondria. NADH and FADH2 produced from the tricarboxylic acid cycle transfer to the mitochondria, where they serve as electron donors to the mitochondrial membrane-associated redox enzyme complexes. The electrons (e−) are shuttled through oxidoreductase complexes I, II, III and IV (cytochrome c), until they are donated to molecular oxygen, forming water. The electron transfer into complexes I, III and IV by NADH (and FADH2 via complex II to complex III) produces a proton gradient at the outer mitochondrial membrane, generating a potential between the inner mitochondrial membrane and outer mitochondrial membrane. This potential drives ATP synthesis, and is crucial for mitochondrial viability, function, and normal metabolism. As electrons are passed from complex II to complex III, however, ROS are produced as by-products. The levels of ROS produced during normal oxidative phosphorylation are minimal, and they are detoxified by cellular antioxidants such as glutathione, catalase and superoxide dismutase. The hyperglycemic cell, on the other hand, shuttles more glucose through the glycolytic and tricarboxylic acid cycles, providing the cell with an over-abundance of NADH and FADH2 electron donors. This produces a high proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which increases the turnover of the initial complexes, and thereby produces increased levels of radicals. Accumulation of these radicals, or ROS, is severely detrimental to mitochondrial DNA, mitochondrial membranes and the whole cell. Abbreviations: Cyto-c, cytochrome c; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; e−, electrons; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; O2•−, superoxide; Pi, phosphate; SOD, superoxide dismutase.
