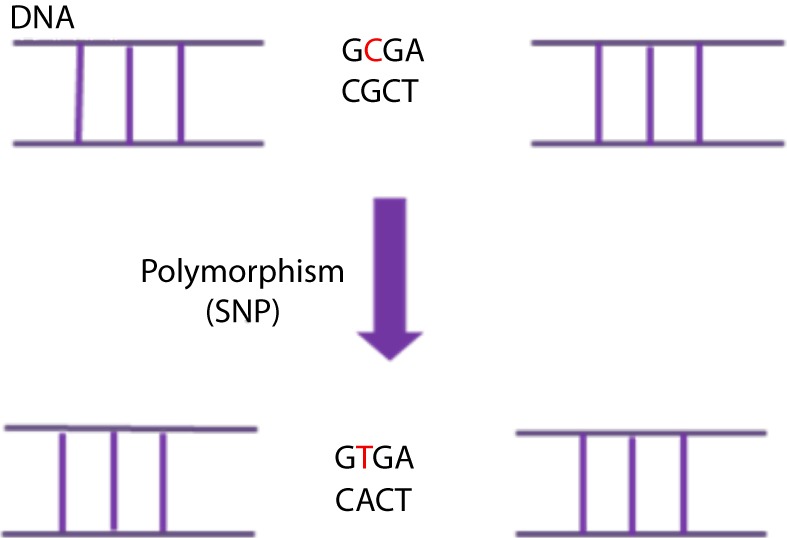
Figure 7. A Single-Nucleotide DNA Polymorphism (SNP) is defined as a single DNA variation detected when a single nucleotide in the genome (or other common sequence) is different between species or paired chromosomes in an individual. In this case there is a substitution of a C (Cytosine) in a T (Tymine) which causes the change of a G (Guanine) in a A (Adenine) in the complementary DNA strand.