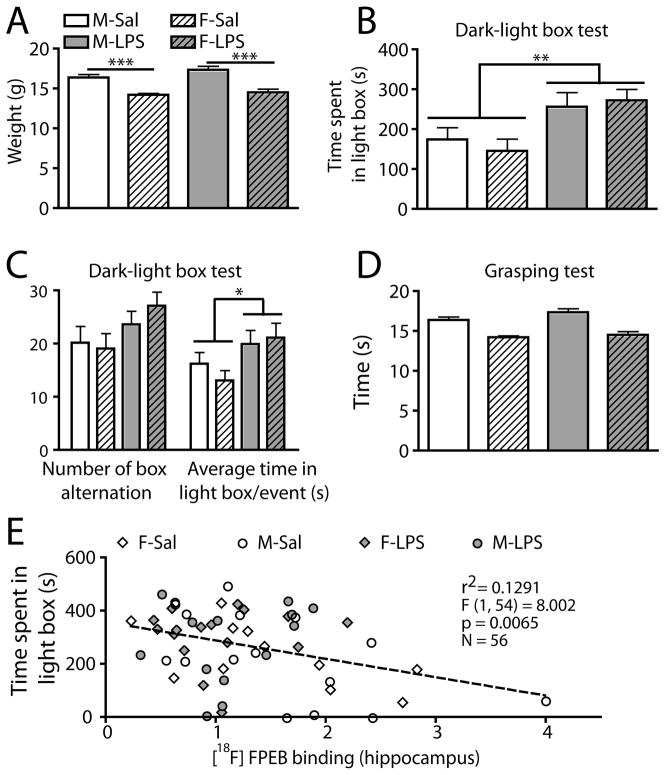
Figure 4.
Reduction of unconditioned anxiety level in adolescent offspring prenatally exposed to LPS.
(A) LPS prenatal exposition did not change the weight of offspring at PnD30. (B) Dark-light box test showed that both males and females exposed to LPS spent more time in the light compartment. (C) Further analysis showed that the number of box alteration did not significantly change in LPS-treated offspring. However, LPS-exposed offspring spent more time per exploratory event in the light box. (D) Grasping ability was similar between all groups. (E) The binding level of [18F]FPEB in hippocampus correlated negatively with the time spent in the light box. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). Correlation was determined by linear regression analysis. Each dot represents a single animal. For panel A to D, the number of males and females was 25–29 and 22–23 for saline group, whereas it was 20 and 19–20 for LPS group. Abbreviations: M-Sal, male-saline; F-Sal, female-saline; M-LPS, male-LPS; F-LPS, female-LPS. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01