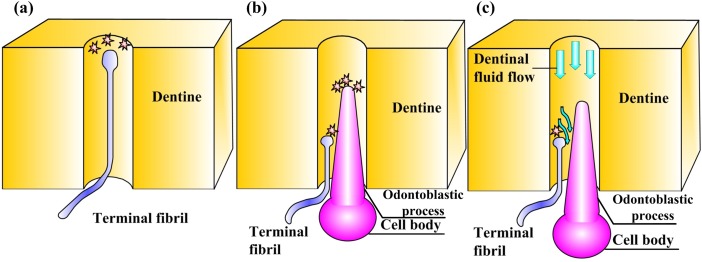
Fig. 3.
The three dominant hypotheses explaining differences between pain associated with heating and cooling. (a) The neural theory, in which differences arise from hot- and cold-sensitive ion channels on the terminal fibril of a nociceptor; (b) the odontoblastic transduction theory, in which signals transduced by odontoblasts are conveyed to the terminal fiber of a nociceptor; (c) the hydrodynamic theory, in which thermally induced dentinal fluid flow over the terminal bead of a nociceptor plays an important role in thermal pain transduction.