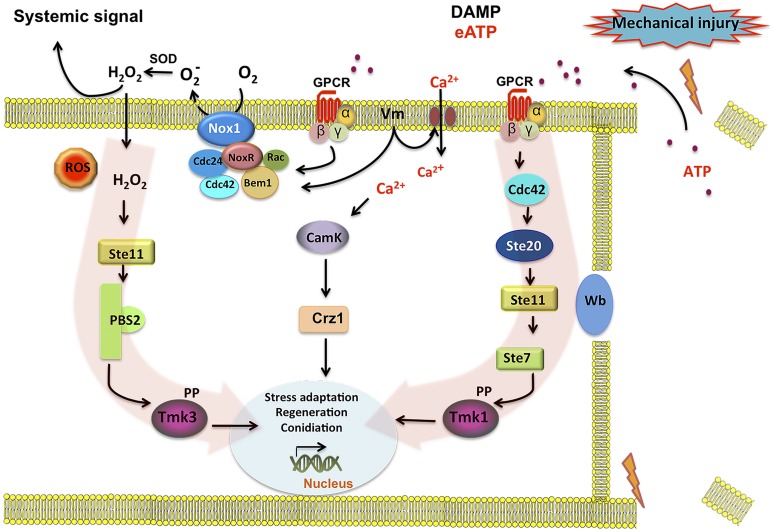
FIGURE 6.
Model for injury-induced signaling in Trichoderma atroviride. Broken hyphae release ATP as a signal molecule. ATP is perceived by a putative G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) activating the Tmk1 and Tmk3 MAPK pathways (highlighted by red arrows). Activation of the GPCR turns on the Cdc42 GTPase in coordination with an increase of Nox1-dependent reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. Cdc42 may in turn activate the Ste20 MAPK pathway, leading to Tmk1 phosphorylation. In a parallel pathway increases in intracellular calcium and CamK kinases, regulate targets required for the damage response. Calcium influx may also lead to changes in membrane potential (Vm) and/or directly activate the Rac GTPase component of the NADPH oxidase (Nox1/NoxR) complex, generating . A superoxide dismutase (Sod) converts into H2O2 that can diffuse into the cell, activating the Ste11 MAPK pathway, leading to Tmk3 phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of Tmk1 and/or Tmk3 results in the activation of the developmental program that results in the formation conidia.