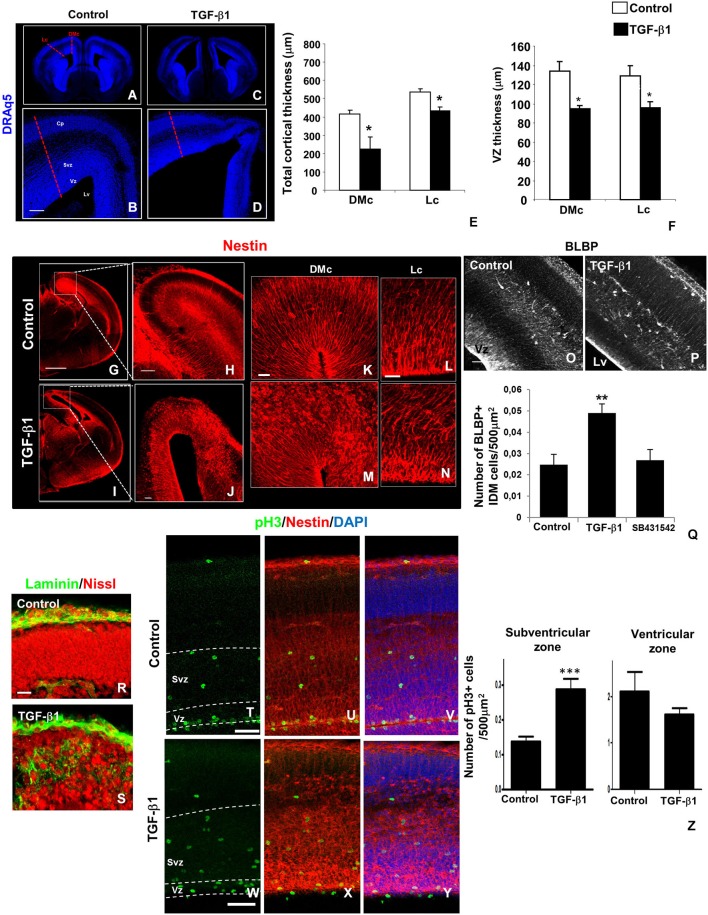
Figure 2.
TGF-β1 injection affects cerebral cortex and RG morphology. In utero intraventricular injection of TGF-β1 in mouse embryos (injection at E14 and analysis at E16) promoted several morphological alterations in the cerebral cortex wall in lateral (Lc) and dorsomedial (DMc) cortex areas (A–D). TGF-β1 reduces the thickness of total cortical area (E) and VZ (F) in both regions. Note that TGF-β1 also disrupted nestin+ (red) radial fiber networks (G–J), an event more prominent at DMc than in Lc (K–N). RG loss of polarity induced by TGF-β1 is accompanied by increase in the numbers of BLBP+ cells (white) with intermediate differentiated morphology (IDM) across cortical wall (O–Q). SB431542 injection does not affect BLBP+ IDM cells numbers. These morphological alterations were followed by basal membrane laminin (green) and neuronal cell bodies (Nissl) ectopic distribution (R,S). TGF-β1 also disorganized pH3+ cells (green) distribution across cortical wall, especially VZ pH3+ cells’ nucleus alignment (T–Y), without affects its numbers (Z), however increased the numbers of pH3+ cells in the SVZ (Z). *P < 0.05, **P < 0,005, ***P < 0005. Scales: 500 μm (G), 100 μm (B,O), 50 μm (H,J,T,W), 20 μm (K,L,R). Cp: cortical plate, Vz: ventricular zone, Svz: subventricular zone, Cx: cortex, Lv: lateral ventricle.