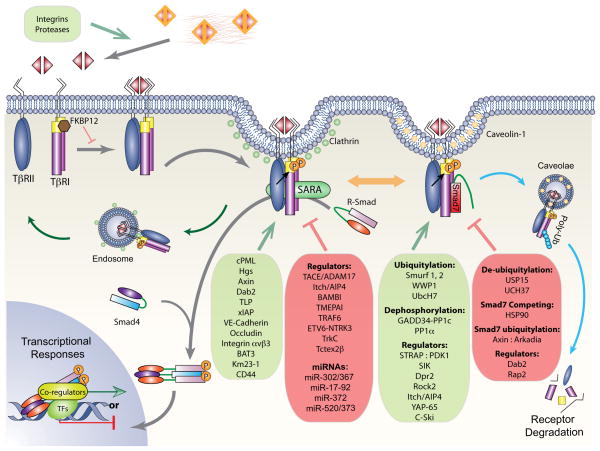
Figure 1. Regulation of the TGF-β receptors.
The TGF-β signaling pathway is outlined in thick gray lines, whereas the endosomal recycling pathway and lipid rafts-caveolae degradation pathway are indicated by green and blue lines, respectively. Binding of ligand stabilizes the heteromeric complex of TβRII and TβRI receptors, resulting in activation of TβRI through phosphorylation of its GS domain by TβRII. R-Smads are then activated by TβRI with SARA as scaffold, and form trimeric complexes with Smad4 that translocate into the nucleus, where they direct transcription responses of target genes. Activated receptor complexes are also internalized through lipid rafts and caveolae, where they are poly-ubiquitylated by E3 ubiquitin ligases recruited by Smad7 and destined for degradation. Various regulators of functional TGF-β receptor complexes are schematically shown. Inhibitory mechanisms are listed in a red box with blunt-headed lines, whereas those that enhance the complexes formation are listed in a green box with arrows.