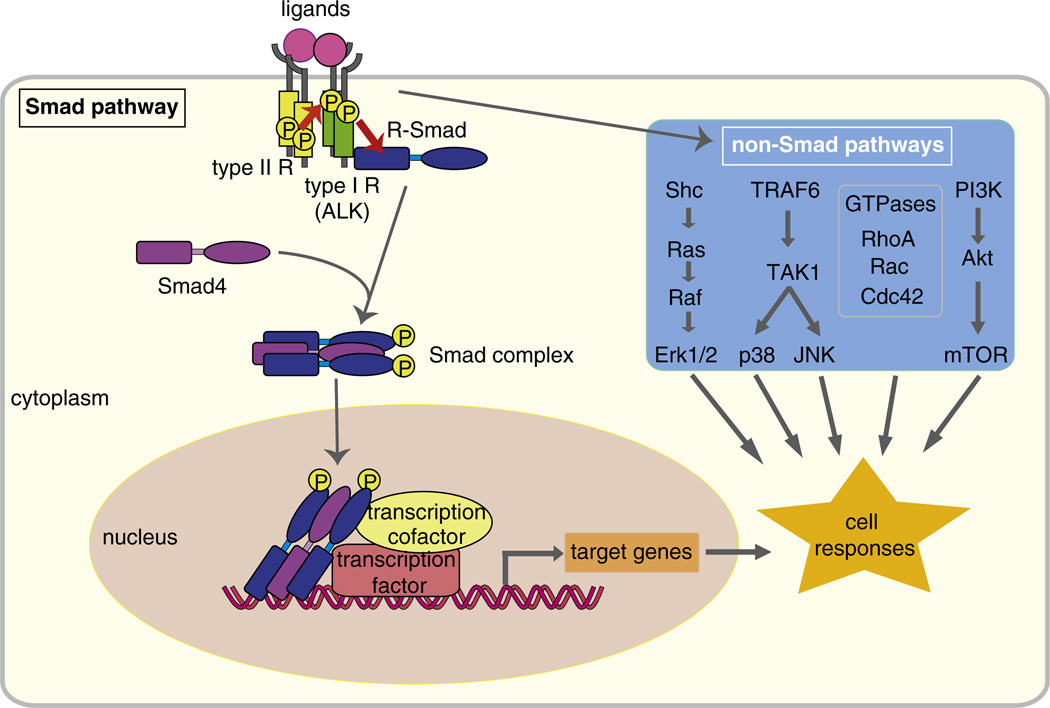
Fig. 2.
Smad-dependent and Smad-independent TGF-β family signaling. Ligands of TGF-β family members bind to type I and type II receptors. Upon ligand binding, the type II receptors phosphorylate the type I receptors, which then phosphorylate and activate effector Smads. The activated Smads form complexes with Smad4, and translocate into the nucleus. The Smad complex interacts with other transcription factors, co-activators or co-repressors to regulate transcription of target genes. TGF-β also elicits activation of other signaling cascades independent of Smad pathways. TGF-β activates the Ras–Raf–MEK–Erk MAPK pathway through tyrosine phosphorylation of ShcA, and p38 and JNK MAPK signaling through activation of TAK1 by the TRAF6. TGF-β also activates the small GTPases Rho, Rac and Cdc42, and the PI3K–Akt pathway.