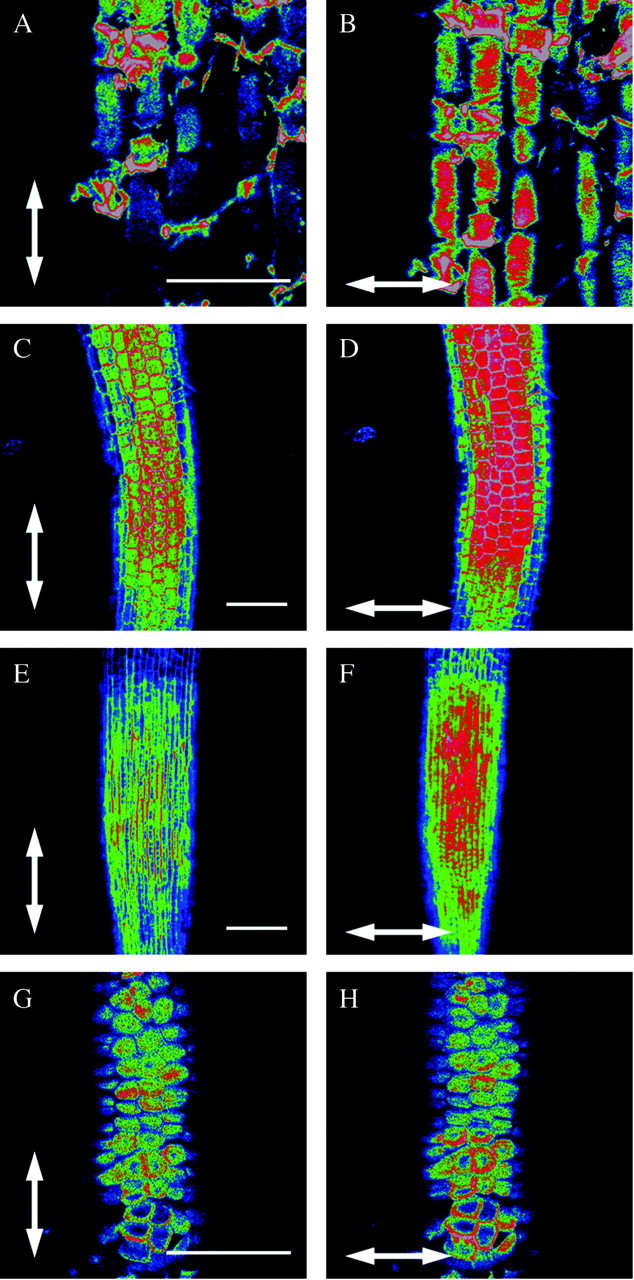
Fig. 3. See Fig. 1 legend for details. In all other species tested belonging either to the commelinoid monocotyledons, the non‐commelinoid monocotyledons or the dicotyledons, the orientation of cellulose fibrils in the outer epidermal wall of the expanding zone of the root is also transverse with respect to the root growth axis (A and B, Transdescantia zebrina Hort. Ex Heynh.: Commelinaceae; C and D, Lemna minor L.: Araceae; E and F, Elsholtzia ciliata (Thunb.) Hyl: Lamiaceae). G and H, The Arecaceae (palms) occupy a special position as their roots show no clear elongation zone and the epidermal cell wall has no preferential orientation of cellulose fibrils. The species shown is Phoenix laureirii Kunth. Scale bars = 100 µm.
