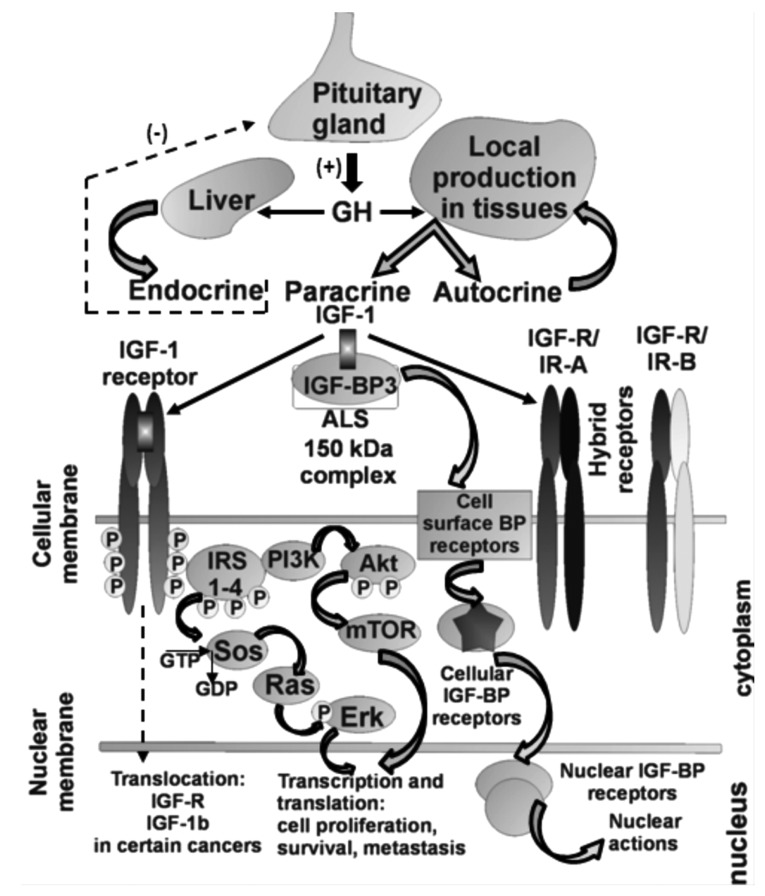
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of IGF-1 axis actions. For simplicity only major IGFBP is shown (IGFBP3) forming a 150-kDa complex with the IGF-1 ligand and ALS (acid labile subunit). Notably, all 3 components of the IGF-1 axis can be translocated to the nucleus: i) IGF-1 (B isoform containing a nuclear localization signal at C-terminus of the E peptide, precise function unknown); ii) IGF-1R as demonstrated in renal cancer, probably involved in transcription regulation; iii) IGFBPs can be translocated to the nucleus via their nuclear receptors and have functions independent of IGF-1 and IGF-1R. Hybrid receptors (IGF-R/IR-A and IGF-R/IR-B) are also activated with lower affinity by IGF-1 ligand as compared to IGF-1R.