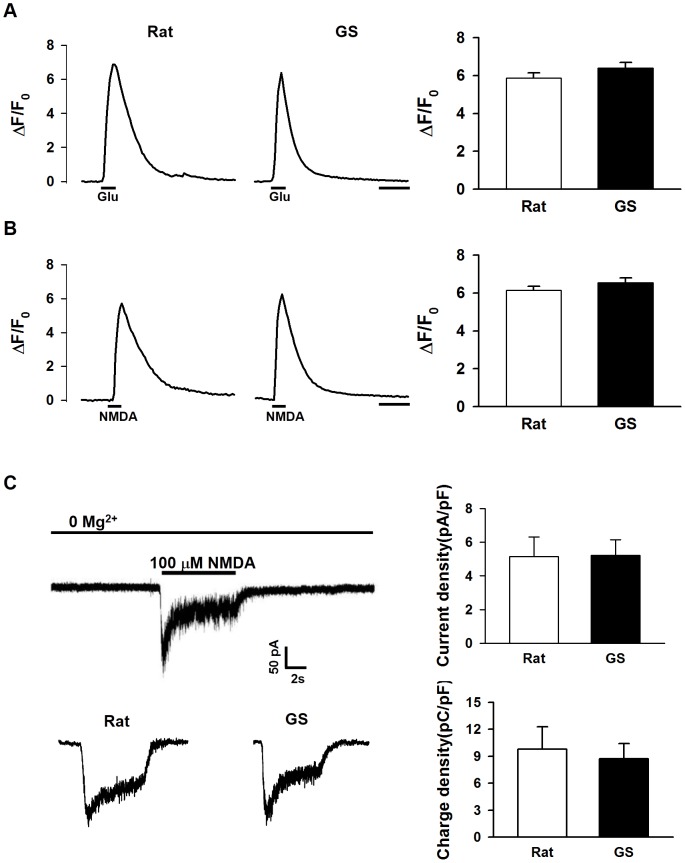
Figure 3. A similar [Ca2+]i elevation in rat and ground squirrel neurons was induced by glutamate and NMDA.
(A) Glutamate (Glu, 200 µM) induced [Ca2+]i changes in ground squirrel and rat neurons. n = 58–65 neurons, from 3 separate experiments. Scale bar, 10 s. (B) NMDA (100 µM) induced [Ca2+]i elevation in both types of neurons. Scale bar, 10 s. The results show that the elevation in [Ca2+]i induced by glutamate or NMDA is similar in the two types of neurons. n = 55–62 neurons, from 3 separate experiments. (C) The neuronal response to NMDA perfusion was measured by whole-cell patch clamp. The results show that no significant differences exist in current density or charge density between ground squirrel and rat neurons. Eighteen rat neurons (from 5 separate experiments) and 26 ground squirrel neurons (from 7 separate experiments) were examined and used for statistical analysis. Fluo-4 AM was used in A and B as a calcium indicator.