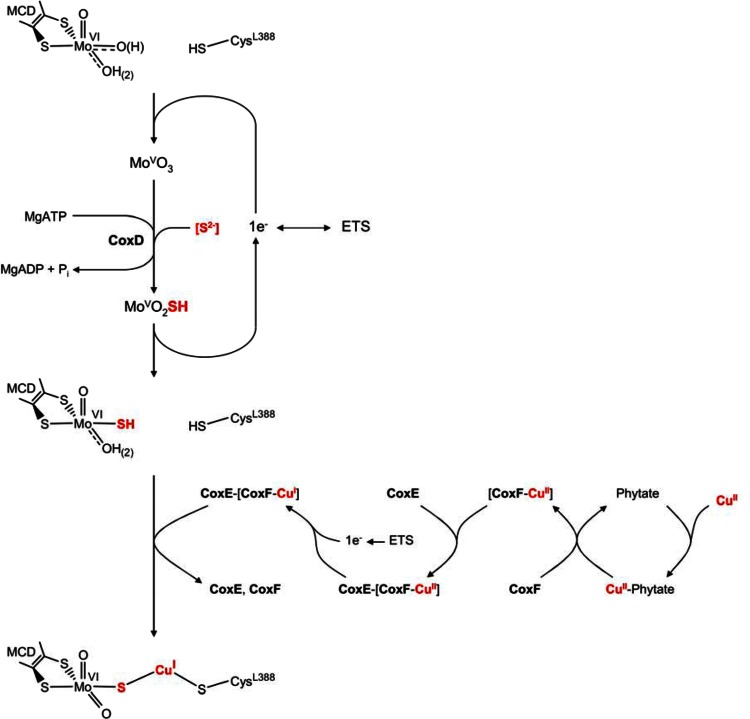
Fig. 9.
Model showing proposed functions of the proteins CoxD, CoxE and CoxF in the assembly of the Mo- and Cu-containing cluster in the active site of folded apo-CO dehydrogenase. CoxD is an AAA+-ATPase chaperone required for the sulfuration of the trioxo-Mo ion. CoxF, which is attached to the cytoplasmic membrane through complex formation with the von Willebrand protein CoxE, introduces a Cu1+-ion resulting in a catalytically competent [CuSMoO2] center. CoxF employs suspected phytase activity for the release of Cu2+ attached to phytate and a putative Cu-binding motif to escort the metal ion. The respiratory electron transport system (ETS) supplies electrons for the generation of Cu1+ from Cu2+. See the text for further explanations