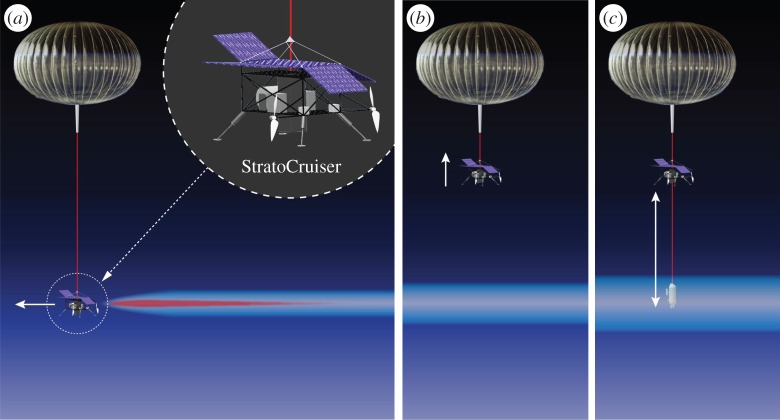
Figure 4.
The concept of operations for the proposed experiment is initiated by seeding a 1 km length of stratospheric air with a combination of water vapour and sulfate aerosol using the propulsive capability of the StratoCruiser (a). Using a combination of its altitude and propulsive capabilities, the StratoCruiser manoeuvres past and above the seeded volume, which continues to expand owing to the turbulent wake generated by the propellers. The suspended instrument payload is reeled through the seeded volume to measure aerosols, water vapour and chemical species including HCl and ClO (b). The propulsion capability together with the LIDAR surveillance is used to track the seeded volume as it drifts with ambient wind and to make repeated measurements with the suspended payload, resolving the chemical evolution within the seeded volume as a function of time (c).