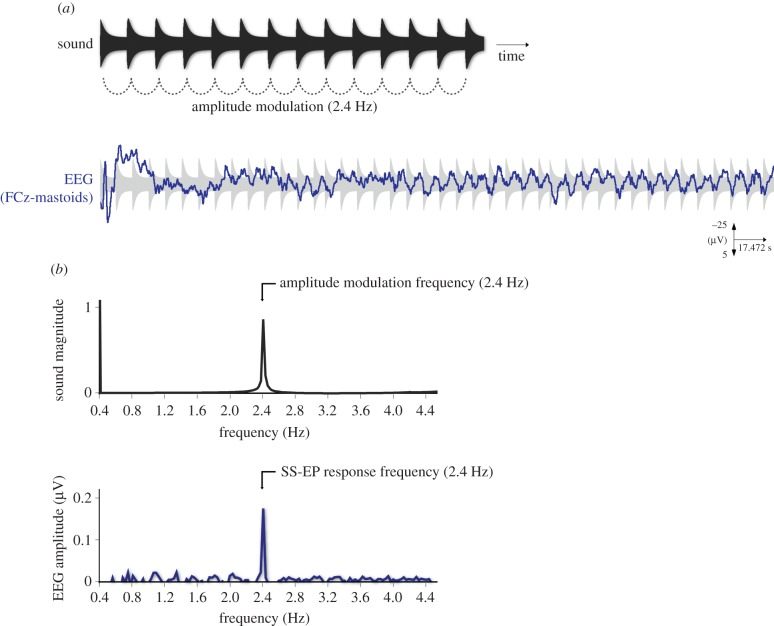
Figure 1.
(a) Sound envelope excerpt of a pure tone amplitude-modulated periodically at 2.4 Hz (upper graph) and EEG response to this sound as obtained from electrode FCz (fronto-central electrode) from the average across 10 participants (band-pass filtered between 0.3 and 30 Hz). Typical transient evoked potentials are elicited at the onset of the sound, but after a few seconds the entrainment of the EEG to the periodic amplitude modulation becomes visible. (b) Envelope spectrum of this sound, with peak of intensity magnitude at 2.4 Hz (here, normalized between 0 and 1; upper panel), and the corresponding EEG spectrum averaged across 10 participants and across the 64 channels, with peak of EEG amplitude (i.e. the SS-EP elicited in response to the periodic sensory stimulation) at 2.4 Hz. Adapted from [32]. (Online version in colour.)