Figure 4.
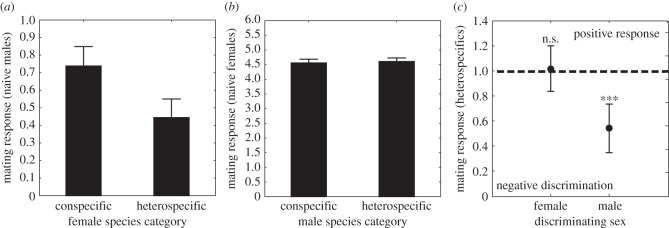
Mate responses of sexually naive C. splendens males and females towards con- and heterospecific mates of the opposite sex. (a) Mean (±s.e.) mate responses of sexually naive C. splendens males towards conspecific females and heterospecific females. These sexually naive males showed a significantly lower response towards heterospecific females, compared with their response towards conspecific females (paired t-test: t1,29 = 2.713; p = 0.011). (b) Mean (±s.e.) mate responses of sexually naive C. splendens females towards conspecific and heterospecific males. There was a significant effect of female population origin (Klingavälsån or Höje Å) on mean mate responses (F1,193 = 27.314; p < 0.001), but no there was no significant difference in the strength of naive female responses towards con- and heterospecific males (F1,193 = 0.067; p = 0.80). (c) Comparison between sexually naive female and male C. splendens in their mean response towards heterospecific putative mates (line at 1.0 indicates the average standardized response towards conspecifics). Means (±95 CIs) are shown (data only from Klingavälsån). Sexually naive female C. splendens do not discriminate against heterospecifics mates, unlike sexually naive male C. splendens (ANOVA for effect of sex: F1,60 = 12.903; p = 0.001).
