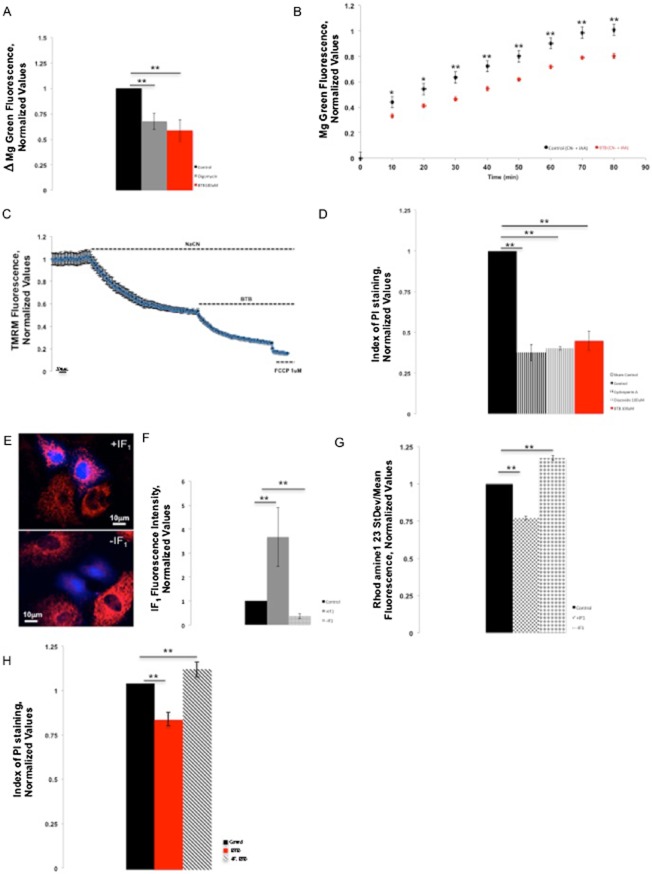
Figure 2.
BTB spares mitochondrial ATP consumption and protects from ischaemic cell death in an IF1-dependent fashion. (A) Indirect assessment of ATP intracellular levels through monitoring of MgG fluorescence in HL-1 cells in conditions when the F1Fo-ATPsynthase is reversed using fluorescence microscopy. The bars show the change of MgG mean fluorescence 12 min after subsequent addition of BTB or oligomycin B following reversal of the enzyme by rotenone and antimycin A. The inhibitors of the ETC caused an increase in the MgG fluorescence (control), suggesting a decrease in intracellular (ATP) and thus a reversal of the F1Fo-ATPsynthase. BTB and oligomycin significantly reduced this increase in fluorescence, suggesting preservation of ATP through inhibition of the reversed F1Fo-ATPsynthase. Control, n = 26; oligomycin B, n = 30; BTB 100 μM, n = 29. **P < 0.001, significantly different from control. (B) Time course of MgG fluorescence in HeLa cells with and without BTB following inhibition of respiration. At 80 min of NaCN and IAA treatment, n = 8. **P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, significant effects of BTB. (C) Kinetics of ΔΨm dissipation in HeLa cells. TMRM fluorescence values are normalized to the initial baseline; mean data are shown from 3 experiments. (D) Protective effect of BTB against ischaemia/reperfusion in HL-1 cells: compared with the ischaemic control, BTB significantly reduced the cell death ratio after simulated ischaemia/reperfusion, as assessed by the ratio of PI-positive cells over Hoechst-positive cells, similarly to the positive controls of cardioprotection using CsA and diazoxide. Sham control, n = 5; CsA 200 nM, n = 16; diazoxide 100 μM, n = 12; BTB 100 μM, n = 5. **P < 0.001, significantly different as shown. (E) Immunofluorescence assay confirming an efficient IF1 overexpression or silencing. (F) Quantification of the efficiency of modulation of IF1 in HL-1 cells. n = 5; **P < 0.001, significantly different from control. (G) Effect of the modulation of IF1 expression on the efficiency of BTB in conditions of reversion of the F1Fo-ATPsynthase in HL-1 cells loaded with Rh123 using fluorescence microscopy. The ΔΨm was monitored using the SD/mean fluorescence ratio. Similarly to Figure 1E, the bars show the change in ΔΨm 15 min after the addition of BTB when the F1Fo-ATPsynthase was reversed by rotenone and antimycin A. Addition of BTB in +IF1 cells resulted in a potentiation of its effect on ΔΨm (mitochondrial depolarization) compared with non-transfected HL-1 cells, suggesting that overexpression of IF1 potentiated the effect of BTB while silencing of IF1 (–IF1) reduced its effect. n = 112; **P < 0.001, significantly different from control. (H) Histogram of BTB-mediated protection in HeLa cells from ischaemic cell death, scored by PI staining. **P < 0.001, significantly different from control.