Figure 3.
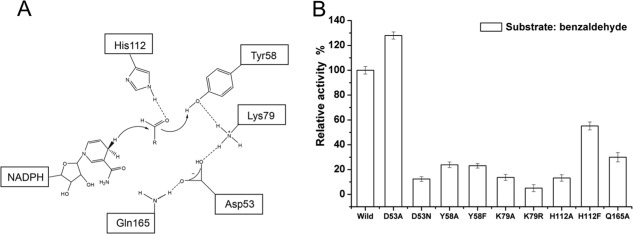
The proposed catalytic mechanisms and reductive activity determined for AKR5C3 mutants. (A) Schematic representation of NADPH-dependent reduction of the carbonyl group. Hydride transfer occurs from the pro-R-hydrogen of NADPH to the carbonyl group of substrate, whereas C carbonyl is polarized by both Tyr58 and His112. Dashed lines show hydrogen bond network. (B) The relative activity of AKR5C3 and its mutants using benzaldehyde as substrate. The enzyme activity was measured as described in “Materials and methods”. The reaction mixture contains 0.05M potassium phosphate (pH 6.5), 1 mM NADPH and 2.5 mM substrate, initiated at 30°C by the addition of NADPH. One unit enzyme activity was defined as the amount of enzyme activity catalyzing the conversion of 1.0 µmol pyridine nucleotide per minute at optimum temperature. The 100% activity of wild AKR5C3 with benzaldehyde was 2.91 U mg−1.
