Figure 1.
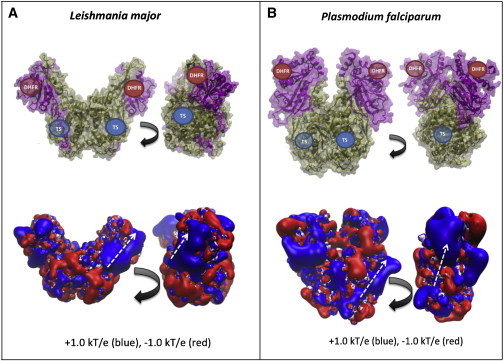
Structures of L. major (A) and P. falciparum DHFR-TS (B), showing TS and DHFR active sites (upper images) and electrostatic potential visualizations (lower images). The approximate location of the TS and DHFR active sites are labeled, with transparent circles representing the active-site labels that are obscured in the current view of the enzyme. White lines indicate hypothesized electrostatic-mediated dihydrofolate channeling path between the TS and DHFR active sites on each monomer. The electrostatic potential maps were created with APBS at physiological (150 mM) ionic strength and pH 7.0.
