Figure 4.
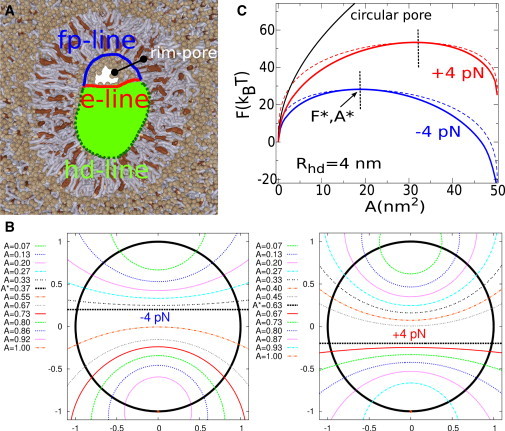
(A) A rim-pore in detail (13). The geometry involves three different types of boundary lines: the hd-line, i.e., the junction between the diaphragm and the vesicular membrane (green); the fp-line, i.e., the upper boundary of the rim-pore corresponding to the partially fused bilayers (blue); and the e-line, i.e., the lower boundary of the rim-pore provided by the free edge of diaphragm (red). (B) Pathway of rim-pore expansion as a function of relative pore area under the conditions λfp − λhd ±1 kT/nm or ±4 pN (for further detail, see Appendix). (Thick, black central circle) Circumference of the HD (i.e., the hd-line and the fp-line). The shape of the e-line is represented by the intersecting, colored circles. The rim-pore expansion proceeds from top to bottom. (C) Free energy of the expanding rim-pore for different values of λfp − λhd. (Black line) Regular circular pore. (Dashed lines) Free energy of a rim-pore; (straight line) e-line. To see this figure in color, go online.
