Table 1 .
Performance of Rubin’s Rules in simulation study
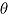 |
Mean 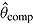
|
Mean 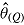
|
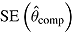 |
Sqrt mean 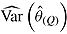
|
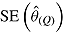 |
RR cover | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “No treatment effect” scenario | |||||||
| MAR | 0.0 | −0.009 | −0.009 | 0.784 | 0.820 | 0.823 | 0.948 |
| copy ref | 0.0 | −0.009 | −0.006 | 0.783 | 0.818 | 0.700 | 0.977 |
| jump to ref | 0.0 | −0.009 | −0.007 | 0.784 | 0.827 | 0.663 | 0.984 |
| copy increm | 0.0 | −0.009 | −0.007 | 0.784 | 0.823 | 0.715 | 0.974 |
| LMCF | 1.6 | 1.592 | 1.594 | 0.846 | 0.876 | 0.828 | 0.961 |
| “Treatment effect” scenario | |||||||
| MAR | −3.0 | −3.019 | −3.020 | 0.778 | 0.820 | 0.818 | 0.948 |
| copy ref | −2.4 | −2.417 | −2.415 | 0.786 | 0.827 | 0.708 | 0.975 |
| jump to ref | −2.4 | −2.417 | −2.415 | 0.787 | 0.835 | 0.668 | 0.983 |
| copy increm | −2.8 | −2.818 | −2.815 | 0.779 | 0.823 | 0.715 | 0.975 |
| LMCF | −1.2 | −1.214 | −1.213 | 0.856 | 0.892 | 0.842 | 0.959 |
Note.
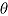 is true treatment effect; mean
is true treatment effect; mean 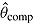 is average of complete-data estimates of
is average of complete-data estimates of 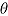 (maximum Monte Carlo standard error = 0.0086); mean
(maximum Monte Carlo standard error = 0.0086); mean 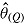 is average of RR treatment effect estimates (max MCSE = 0.0084);
is average of RR treatment effect estimates (max MCSE = 0.0084); 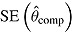 is empirical standard error of complete-data estimates (max MCSE = 0.0061); sqrt mean
is empirical standard error of complete-data estimates (max MCSE = 0.0061); sqrt mean 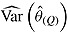 is square root of the average RR estimate of the variance (max MCSE = 0.0005);
is square root of the average RR estimate of the variance (max MCSE = 0.0005); 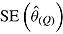 is empirical standard error of RR estimate (max MCSE = 0.0060); RR cover is coverage of 95% confidence interval from Rubin’s Rules (max MCSE = 0.0022).
is empirical standard error of RR estimate (max MCSE = 0.0060); RR cover is coverage of 95% confidence interval from Rubin’s Rules (max MCSE = 0.0022).
