Figure 2.
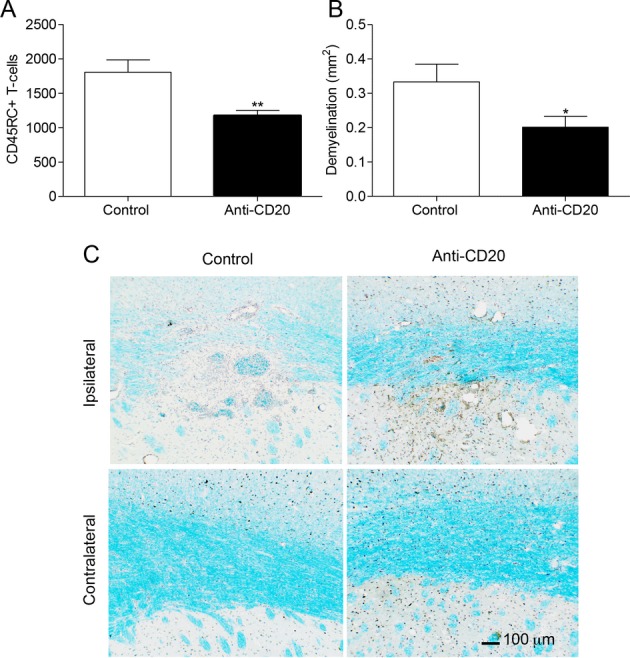
Anti-CD20 treatment reduces T-cell infiltration and demyelination in the fDTH-EAE model of MS. (A) Number of CD45RC+ T-cells in the lesion in the control animals (n = 9) and the anti-CD20-treated animals (n = 9), **P = 0.005. (B) Area of myelin loss within the lesion measured using Luxol fast blue staining in both the control animals (n = 10) and anti-CD20-treated animals (n = 9), *P = 0.049. (C) Photomicrographs demonstrating the greater loss in Luxol fast blue staining (light blue) in the control animals compared to the treated animals at the site of the lesion. A similar loss is not observed in the contralateral hemisphere (not shown). Nuclei were counter stained with Mayer’s haematoxylin (dark blue and brown). EAE, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis; MS, multiple sclerosis.
