Figure 3.
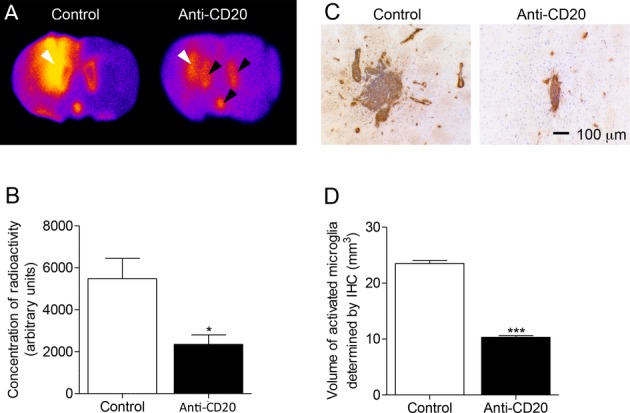
B-cell depletion with anti-CD20 antibody reduces the area of microglial activation in DTH-EAE rat model. (A) In situ hybridization of coronal brain sections with [125I]DPA-713. White arrows indicate the location of the lesion, black arrows demonstrate the binding in the ventricles caused by binding to ependymal cells and the Choroid Plexus. (B) [125I]DPA-713 binding in DTH-EAE lesions (Control, n = 5, anti-CD20 n = 6), *P = 0.012. (C) Immunohistochemistry showing the area of OX-6+ (MHCII, brown staining) staining surrounding a typical lesion in both a control animal and anti-CD20-treated animal. Nuclei visualized using cresyl violet (blue). (D) Volumetry of lesions calculated by measuring the area of OX-6 staining throughout the lesion (Control, n = 9; anti-CD20, n = 10), ***P < 0.001. EAE, experimental allergic encephalomyelitis.
