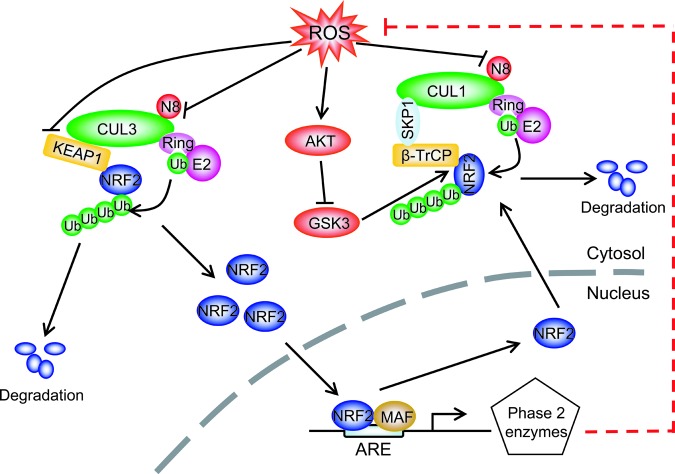
FIG. 3.
Redox regulation of NRF2 via CRL E3s: Under normal physiological conditions, the NRF2 level is kept low as a result of targeted degradation by (i) CRL3 upon Keap1 binding and (ii) CRL1 upon β-TrCP binding, following GSK3-mediated NRF2 phosphorylation. Under oxidative stressed conditions, ROS on one hand inhibits cullin neddylation to inactivate CRLs and on the other hand activates AKT to block GSK3-mediated NRF2 phosphorylation, leading to suppression of NRF2 degradation. Accumulated NRF2 then translocates into the nucleus, where it complexes with MAF to bind to the ARE and transactivates the expression of antioxidant enzymes to scavenge ROS. ARE, antioxidant response element; GSK3, glycongen synthase kinase 3; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; ROS, reactive oxygen species. To see this illustration in color, the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertpub.com/ars