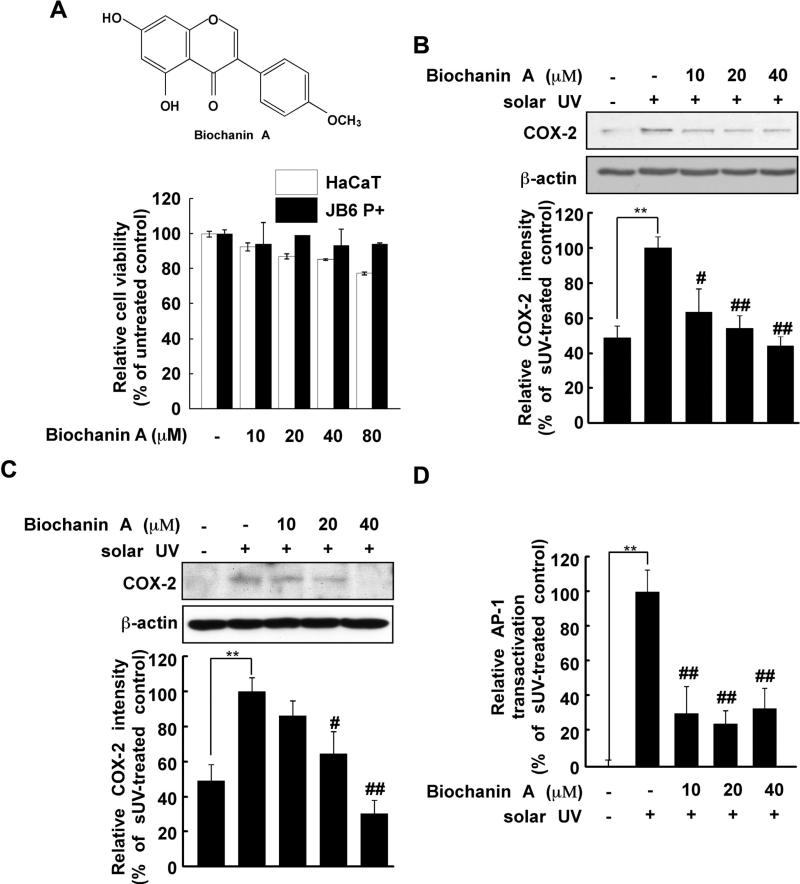
Fig. 1.
Effects of biochanin A on solar UV (sUV) induced cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 expression. (A) Chemical structure of biochanin (upper) and cytotoxicity of biochanin A against HaCaT and JB6 P+ cells (lower). The procedure for evaluating cytotoxicity is described in Section 2. (B) and (C) Biochanin A inhibits sUV-induced COX-2 expression in human HaCaT (B) and mouse JB6 P+ (C) cells. After treatment with biochanin A (0, 10, 20, or 40 μM) for 1 h, 2 the cells were irradiated with solar UV (sUV; 90 kJ/m2) and harvested after 1 h. The protein levels of COX-2 and β-actin were measured by Western blotting. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments that provided similar results. The level of β-actin was detected to verify equal loading of proteins. COX-2 expression was quantified using the Image J software program. (D) Biochanin A inhibits sUV-induced AP-1 transactivation in HaCaT cells. After treatment with biochanin A (0, 10, 20, or 40 μM) for 1 h, HaCaT cells transfected with an AP-1 luciferase plasmid were irradiated with sUV. Data are normalized to the transactivation of sUV-irradiated HaCaT cells (100%). The pound (# and ##) signs indicate significant differences at p < 0.01 and 0.001, respectively, compared to the sUV-treated group. The asterisks (**) indicate a significant induction of COX-2 (B, C) and AP-1 activity (D) induced by sUV. Representative blots from triplicate experiments with similar results are shown.