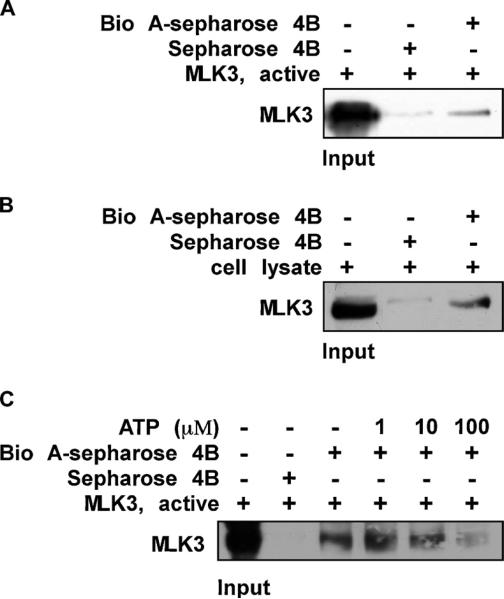
Fig 4.
Biochanin A directly binds to MLK3 in an ATP-competitive manner. (A) the MLK3-biochanin A binding in vitro was confirmed by immunoblotting using an antibody against MLK3; first lane (input control), MLK3 protein standards; second lane (control), Sepharose 4B used to pull down MLK3 as described in Section 2; third lane, MLK3 pulled down using biochanin A–Sepharose 4B affinity beads. (B) the MLK3-biochanin A binding ex vivo was investigated by immunoblotting using an antibody against MLK3; first lane (input control), whole-cell lysate from HaCaT cells; second lane (control), a lysate of HaCaT cells precipitated with Sepharose 4B beads as described in Section 2; third lane, whole-cell lysate from HaCaT cells precipitated by biochanin A–Sepharose 4B affinity beads as described in Section 2. (C) ATP at concentrations of 1, 10, or 100 μM was incubated with the MLK3 active protein for 1 h. Then the MLK3 protein was precipitated with biochanin A– Sepharose 4B affinity beads as described in Section 2. Representative blots from duplicate experiments with similar results are shown.