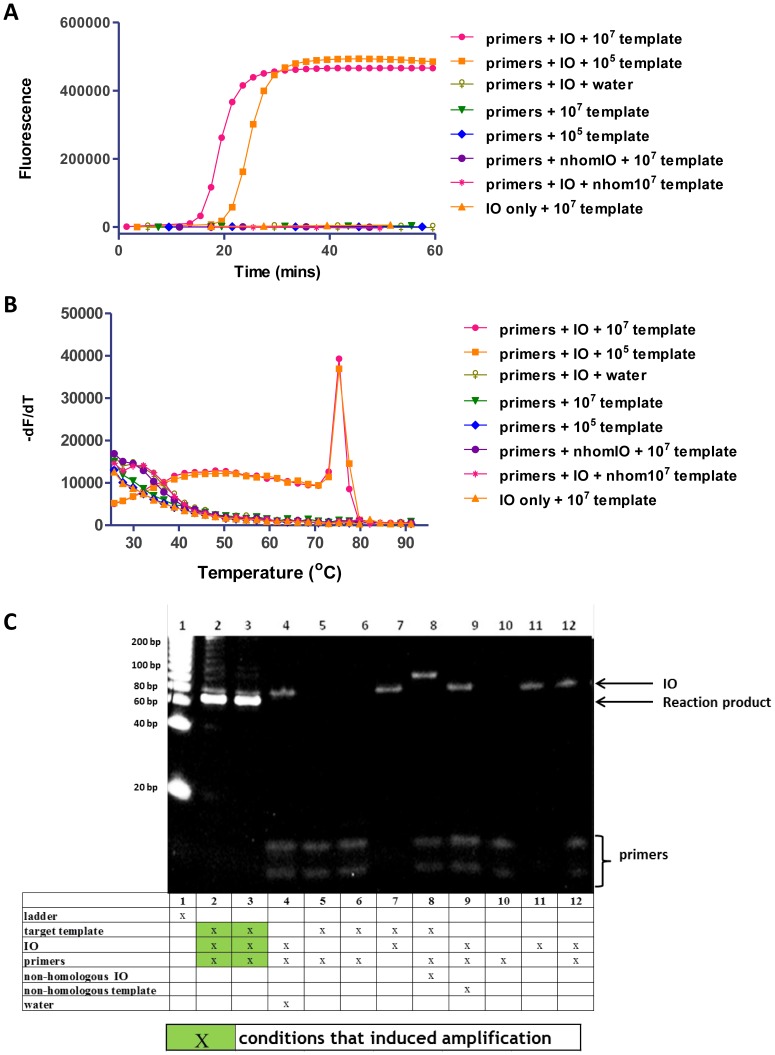
Figure 2. SIBA primers are unable to amplify target DNA independently of the invasion oligonucleotide (IO).
(A) Real-time monitoring of amplification using SYBR Green I, (B) melting curve analysis ((-dF (fluorescence)/dT (temperature) versus temperature), and (C) non-denaturing electrophoresis of the corresponding reaction products. Lane 1, BioRad EZ Load 20 bp Molecular Ruler (20–1000 bp); lane 2, primers + IO + template (107 copies); lane 3, primers + IO + template (105 copies); lane 4, primers + IO + water; lane 5, primers + template (107 copies); lane 6, primers + template (105 copies); lane 7, IO + template (107 copies); lane 8, primers + non-homologous IO + template (107 copies); lane 9, primers + IO + non-homologous template (107 copies); lane 10, 200 nM primers in the absence of SIBA reaction reagents; lane 11, 200 nM IO in the absence of SIBA reaction reagents; lane 12, 200 nM primers and 200 nM IO in the absence of SIBA reagents. Lanes 10–12 served as controls for monitoring the presence of oligonucleotides in the reaction products. These were diluted in TBE buffer and run alongside the SIBA reaction products. SB-F21 and SB-R21 are the forward and reverse primers, respectively. The IO used was SB-IO. The homologous target DNA used was SB-template. nhom = non-homologous to the target template (SB nhom template) or non-homologous IO (SB nhom IO).