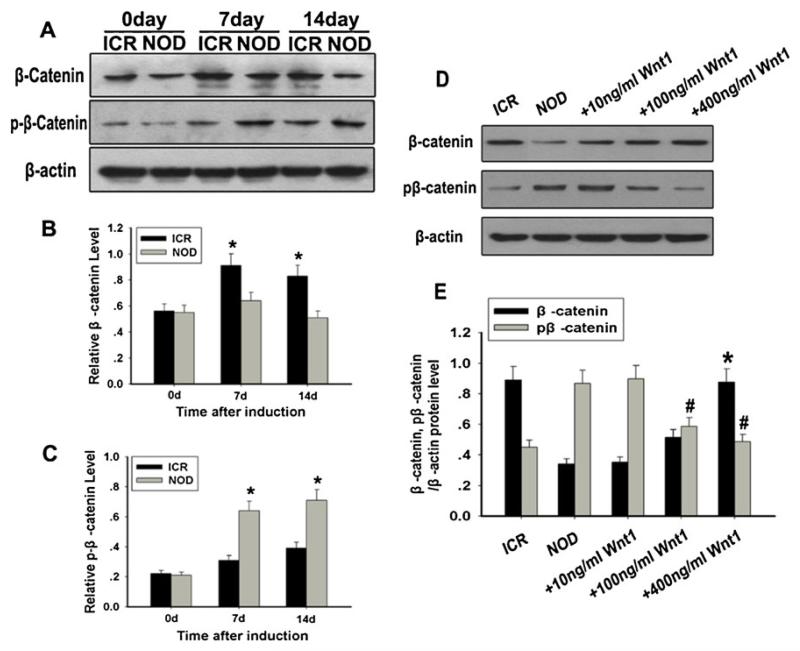
Fig. 3.
Analysis of the expressions of β-catenin and phosphorylated β-catenin. a Western blot analysis of β-catenin and phosphorylated β-catenin expressions. β-Actin was used as the internal control. b Quantification of β-catenin protein levels. c Quantification of phosphorylated β-catenin protein levels. At the 7th and 14th day, decreased expression of β-catenin and increased expression of phosphorylated β-catenin were clearly detected in the NOD-MSCs compared with that in the ICR MSCs (*P<0.05; n=5). d Western blot analysis of β-catenin and phosphorylated β-catenin expressions in neural induction medium with recombinant human Wnt1 (10–400 ng/ml) for 14 days. e Quantification of β-catenin and phosphorylated β-catenin protein levels after treatment with Wnt1. Only treatment with high Wnt1 concentrations (100 and 400 ng/mL) significantly increased the expression of β-catenin and decreased the expression of phosphorylated β-catenin (*P<0.05, #P<0.05; n=5)