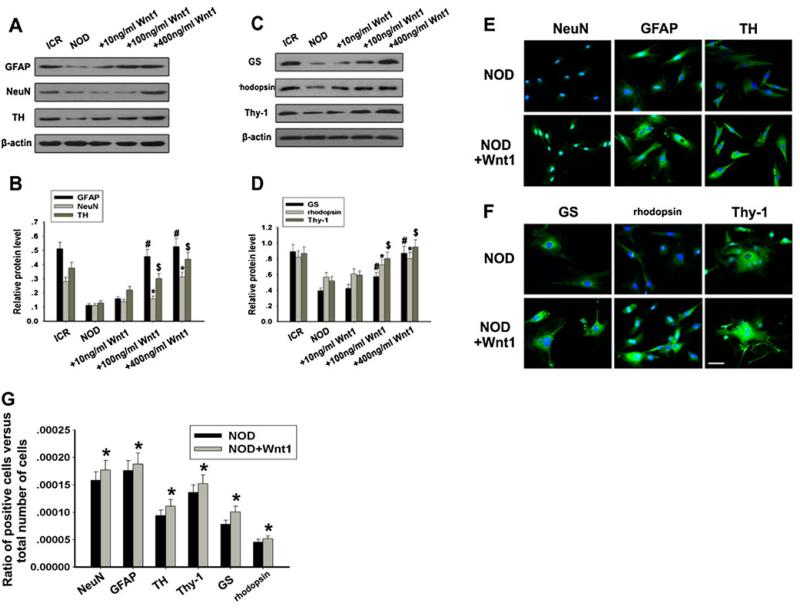
Fig. 7.
Effects of Wnt1 on NOD-MSCs retinal neuron-like differentiation. a Western blot analysis of GFAP, NeuN, and TH expressions after treatment with Wnt1 (10–400 ng/ml). b Quantification of GFAP, NeuN, and TH protein levels after treatment with Wnt1 (10–400 ng/ml). c Western blot analysis of Thy-1, GS, and rhodopsin expressions after treatment with Wnt1 (10–400 ng/ml). d Quantification of Thy-1, GS, and rhodopsin protein levels after treatment with Wnt1 (10–400 ng/ml). After neural induction with recombinant human Wnt1 (10–400 ng/ml) for 14 days Wnt1 concentrations >100 ng/mL were sufficient to increase GFAP, NeuN, TH, Thy-1, GS, and rhodopsin expressions in NOD-MSCs (*P<0.05, #P<0.05, $P<0.05; n=5). e Immunofluorescence staining of GFAP (green), NeuN (green), and TH (green). Blue Hoechst stain. f Immunofluorescence staining of Thy-1 (green), GS (green), and rhodopsin (green). Blue Hoechst stain. g Quantitative evaluation of differentiated ratio after treatment with recombinant human Wnt1 (10–400 ng/ml) for 14 days: NOD-MSCs versus ICR-MSCs. The ratio of positive cells versus total number of cells in the culture: comparison of NOD-MSCs and ICR-MSCs. In this study, GFAP-, NeuN-, TH-, Thy-1-, GS-, and rhodopsin-positive cells were counted 14 days after induction (*P<0.05; n=5). After treatment with 400 ng/mL Wnt1, the levels of these proteins significantly increased in NOD-MSCs. Scale bar=25 μm