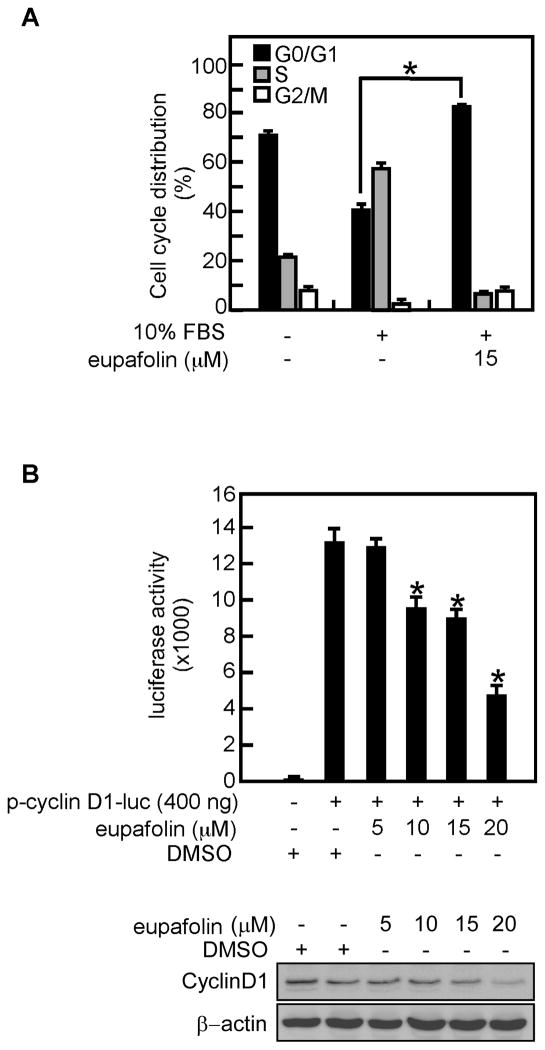
Fig. 3.
Eupafolin causes cell cycle arrest at G1. A, PC3 prostate cancer cells were serum-starved for 16 h to synchronize at G0 phase and then pretreated with eupafolin for 2 h followed by stimulation with 10% FBS including eupafolin for 16 h. The cell cycle distribution was measured by flow cytometry with propidium iodide. Data are expressed as the percentage of cells in G1/G0, S, or G2/M and are shown as means ± S.D. of values from triplicate experiments. B, eupafolin inhibits cyclin D1 transcriptional activity. The inhibitory effect of eupafolin on cyclin D1 activity was measured by introducing cyclin D1 reporter plasmids into PC3 cells followed by treatment with various concentrations of eupafolin. Luciferase activity was measured and data are shown as means ± S.D. of values from triplicate experiments (upper panel). The protein content of cyclin D1was determined by Western blotting (lower panel). The asterisk (*) indicates a significant (p < 0.05) difference in cell cycle distribution (A) or luciferase activity (B) in treated versus untreated cells.