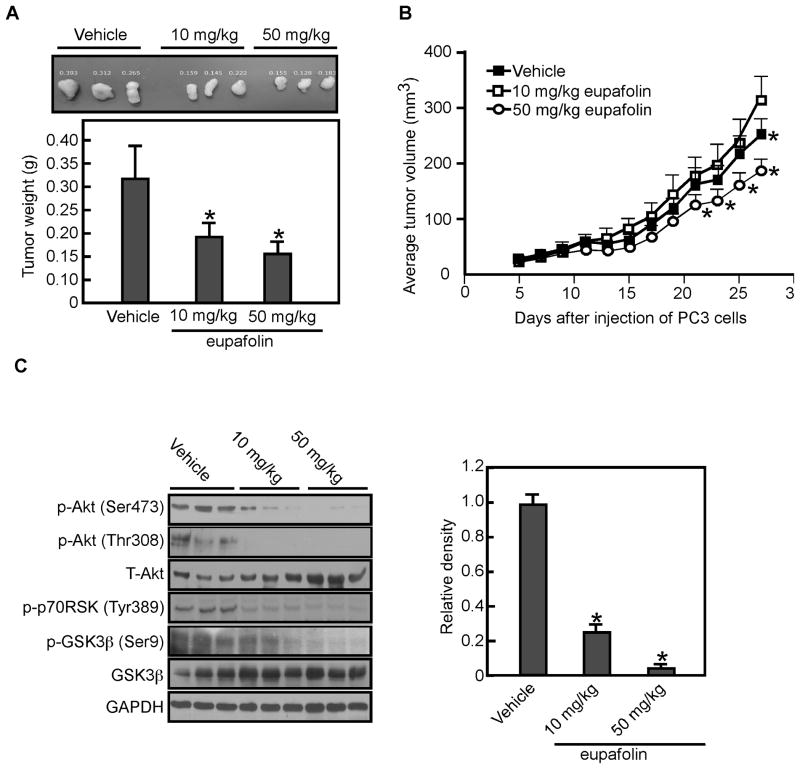
Fig. 6.
Eupafolin suppresses tumor growth in vivo by inhibiting the PI3-K-related signaling pathway. A, the total average tumor weight in the eupafolin-treated groups is significantly less (*, p < 0.05) than that of the vehicle-treated group. Tumors were extracted and weighed after mice were sacrificed. Data are shown as means ± S.D. and significant differences were determined by one-way ANOVA. B, total average tumor volume in the eupafolin-treated group was significantly (*, p < 0.05) less than that of the vehicle-treated group. Tumor volume was measured and recorded 3 times a week throughout the study. Data are shown as means ± S.D. C, the protein levels of total and phosphorylated Akt, p70RSK, and GSK3β were assessed by Western blot analysis in vehicle- and eupafolin-treated tumor tissues. The relative density was compared with actin (lower panel). Data are shown as means ± S.E.